Complete genome sequence of Chitinophaga pinensis type strain (UQM 2034)
- PMID: 21304681
- PMCID: PMC3035255
- DOI: 10.4056/sigs.661199
Complete genome sequence of Chitinophaga pinensis type strain (UQM 2034)
Abstract
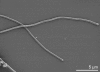
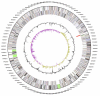
Chitinophaga pinensis Sangkhobol and Skerman 1981 is the type strain of the species which is the type species of the rapidly growing genus Chitinophaga in the sphingobacterial family 'Chitinophagaceae'. Members of the genus Chitinophaga vary in shape between filaments and spherical bodies without the production of a fruiting body, produce myxospores, and are of special interest for their ability to degrade chitin. Here we describe the features of this organism, together with the complete genome sequence, and annotation. This is the first complete genome sequence of a member of the family 'Chitinophagaceae', and the 9,127,347 bp long single replicon genome with its 7,397 protein-coding and 95 RNA genes is part of the Genomic Encyclopedia of Bacteria and Archaea project.
Keywords: GEBA; Gram-negative; aerobic; biomass degrader; chitinolytic; filamentous; gliding; mesophile; myxospores; ‘Chitinophagaceae’.
Figures

References
-
- Sangkhobol V, Skerman VBD. Chitinophaga, a new genus of chitinolytic myxobacteria. Int J Syst Bacteriol 1981; 31:285-293
-
- Sly LI, Taghavi M, Fegan M. Phylogenetic position of Chitinophaga pinensis in the Flexibacter-Bacteroides-Cytophaga phylum. Int J Syst Bacteriol 1999; 49:479-481 - PubMed
-
- Kämpfer P, Young CC, Sridhar KR, Arun AB, Lai WA, Shen FT, Rekha PD. Transfer of [Flexibacter] sancti, [Flexibacter] filiformis, [Flexibacter] japonensis and [Cytophaga] arvensicola to the genus Chitinophaga and description of Chitinophaga skermanii sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2006; 56:2223-2228 10.1099/ijs.0.64359-0 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

