Role of the pJM1 plasmid-encoded transport proteins FatB, C and D in ferric anguibactin uptake in the fish pathogen Vibrio anguillarum
- PMID: 21304833
- PMCID: PMC3034151
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1758-2229.2009.00110.x
Role of the pJM1 plasmid-encoded transport proteins FatB, C and D in ferric anguibactin uptake in the fish pathogen Vibrio anguillarum
Abstract
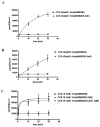
Vibrio anguillarum serotype O1 is part of the natural flora in the aquatic habitat, but under certain circumstances it can cause terminal haemorrhagic septicemia in marine and fresh water fish due to the action of the anguibactin iron uptake system encoded by the virulence plasmid pJM1. This plasmid harbours the genes for the biosynthesis of the siderophore anguibactin and the ferric anguibactin transport proteins FatD, C, B and A encoded in the iron transport operon. The FatA protein is the outer membrane receptor for the ferric siderophore complex and the FatB lipoprotein provides the periplasmic domain for its internalization, whereas the FatC and D proteins are located in the cytoplasmic membrane and might play a role as part of the ABC transporter for internalization of the ferric siderophore. In this work we demonstrate the essential role of these two inner membrane proteins in ferric anguibactin transport and that the lipo-protein nature of FatB is not necessary for ferric anguibactin transport.
Figures





References
-
- Actis LA, Tolmasky ME, Farrell DH, Crosa JH. Genetic and molecular characterization of essential components of the Vibrio anguillarum plasmid-mediated iron-transport system. J Biol Chem. 1988;263:2853–2860. - PubMed
-
- Actis LA, Tolmasky ME, Crosa LM, Crosa JH. Characterization and regulation of the expression of FatB, an iron transport protein encoded by the pJM1 virulence plasmid. Mol Microbiol. 1995;17:197–204. - PubMed
-
- Actis LA, Tolmasky ME, Crosa JH. Vibriosis. Vol. 3. Cab International Publishing; Wallingford, UK: 1999.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

