Berberine improves glucose metabolism in diabetic rats by inhibition of hepatic gluconeogenesis
- PMID: 21304897
- PMCID: PMC3033390
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016556
Berberine improves glucose metabolism in diabetic rats by inhibition of hepatic gluconeogenesis
Abstract
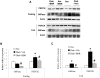
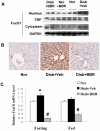
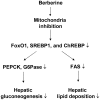
Berberine (BBR) is a compound originally identified in a Chinese herbal medicine Huanglian (Coptis chinensis French). It improves glucose metabolism in type 2 diabetic patients. The mechanisms involve in activation of adenosine monophosphate activated protein kinase (AMPK) and improvement of insulin sensitivity. However, it is not clear if BBR reduces blood glucose through other mechanism. In this study, we addressed this issue by examining liver response to BBR in diabetic rats, in which hyperglycemia was induced in Sprague-Dawley rats by high fat diet. We observed that BBR decreased fasting glucose significantly. Gluconeogenic genes, Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK) and Glucose-6-phosphatase (G6Pase), were decreased in liver by BBR. Hepatic steatosis was also reduced by BBR and expression of fatty acid synthase (FAS) was inhibited in liver. Activities of transcription factors including Forkhead transcription factor O1 (FoxO1), sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c (SREBP1) and carbohydrate responsive element-binding protein (ChREBP) were decreased. Insulin signaling pathway was not altered in the liver. In cultured hepatocytes, BBR inhibited oxygen consumption and reduced intracellular adenosine triphosphate (ATP) level. The data suggest that BBR improves fasting blood glucose by direct inhibition of gluconeogenesis in liver. This activity is not dependent on insulin action. The gluconeogenic inhibition is likely a result of mitochondria inhibition by BBR. The observation supports that BBR improves glucose metabolism through an insulin-independent pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Lee YS, Kim WS, Kim KH, Yoon MJ, Cho HJ, et al. Berberine, a Natural Plant Product, Activates AMP-Activated Protein Kinase With Beneficial Metabolic Effects in Diabetic and Insulin-Resistant States. Diabetes. 2006;55:2256–2264. - PubMed
-
- Kong WJ, Zhang H, Song DQ, Xue R, Zhao W, et al. Berberine reduces insulin resistance through protein kinase C-dependent up-regulation of insulin receptor expression. Metabolism. 2009;58:109–119. - PubMed
-
- Zhang H, Wei J, Xue R, Wu JD, Zhao W, et al. Berberine lowers blood glucose in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients through increasing insulin receptor expression. Metabolism. 2010;59:285–292. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

