A novel soluble immune-type receptor (SITR) in teleost fish: carp SITR is involved in the nitric oxide-mediated response to a protozoan parasite
- PMID: 21305002
- PMCID: PMC3031540
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015986
A novel soluble immune-type receptor (SITR) in teleost fish: carp SITR is involved in the nitric oxide-mediated response to a protozoan parasite
Abstract
Background: The innate immune system relies upon a wide range of germ-line encoded receptors including a large number of immunoglobulin superfamily (IgSF) receptors. Different Ig-like immune receptor families have been reported in mammals, birds, amphibians and fish. Most innate immune receptors of the IgSF are type I transmembrane proteins containing one or more extracellular Ig-like domains and their regulation of effector functions is mediated intracellularly by distinct stimulatory or inhibitory pathways.
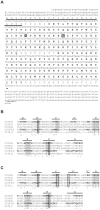
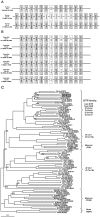
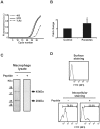
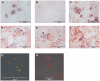
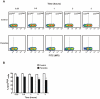
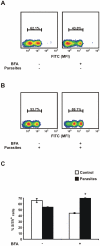
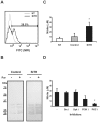
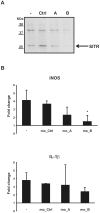
Methodology/principal findings: Carp SITR was found in a substracted cDNA repertoire from carp macrophages, enriched for genes up-regulated in response to the protozoan parasite Trypanoplasma borreli. Carp SITR is a type I protein with two extracellular Ig domains in a unique organisation of a N-proximal V/C2 (or I-) type and a C-proximal V-type Ig domain, devoid of a transmembrane domain or any intracytoplasmic signalling motif. The carp SITR C-proximal V-type Ig domain, in particular, has a close sequence similarity and conserved structural characteristics to the mammalian CD300 molecules. By generating an anti-SITR antibody we could show that SITR protein expression was restricted to cells of the myeloid lineage. Carp SITR is abundantly expressed in macrophages and is secreted upon in vitro stimulation with the protozoan parasite T. borreli. Secretion of SITR protein during in vivo T. borreli infection suggests a role for this IgSF receptor in the host response to this protozoan parasite. Overexpression of carp SITR in mouse macrophages and knock-down of SITR protein expression in carp macrophages, using morpholino antisense technology, provided evidence for the involvement of carp SITR in the parasite-induced NO production.
Conclusion/significance: We report the structural and functional characterization of a novel soluble immune-type receptor (SITR) in a teleost fish and propose a role for carp SITR in the NO-mediated response to a protozoan parasite.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
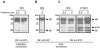

Similar articles
-
Immune-relevant thrombocytes of common carp undergo parasite-induced nitric oxide-mediated apoptosis.Dev Comp Immunol. 2015 Jun;50(2):146-54. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2015.02.008. Epub 2015 Feb 11. Dev Comp Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25681740
-
Differential contribution of neutrophilic granulocytes and macrophages to nitrosative stress in a host-parasite animal model.Mol Immunol. 2008 Jun;45(11):3178-89. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2008.02.025. Epub 2008 Apr 14. Mol Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18406465
-
Nitric oxide hinders antibody clearance from the surface of Trypanoplasma borreli and increases susceptibility to complement-mediated lysis.Mol Immunol. 2009 Oct;46(16):3188-97. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2009.08.011. Epub 2009 Sep 6. Mol Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19735943
-
Nitrosative stress during infection-induced inflammation in fish: lessons from a host-parasite infection model.Curr Pharm Des. 2010;16(38):4194-202. doi: 10.2174/138161210794519138. Curr Pharm Des. 2010. PMID: 21184662 Review.
-
Form, function and phylogenetics of NITRs in bony fish.Dev Comp Immunol. 2009 Feb;33(2):135-44. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2008.09.004. Epub 2008 Oct 7. Dev Comp Immunol. 2009. PMID: 18840463 Review.
Cited by
-
Differential expression and ligand binding indicate alternative functions for zebrafish polymeric immunoglobulin receptor (pIgR) and a family of pIgR-like (PIGRL) proteins.Immunogenetics. 2014 Apr;66(4):267-79. doi: 10.1007/s00251-014-0759-4. Epub 2014 Jan 28. Immunogenetics. 2014. PMID: 24469064 Free PMC article.
-
Multigene families of immunoglobulin domain-containing innate immune receptors in zebrafish: deciphering the differences.Dev Comp Immunol. 2014 Sep;46(1):24-34. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2014.02.004. Epub 2014 Feb 15. Dev Comp Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24548770 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of the Fc-alpha/mu receptor in Xenopus provides insight into the emergence of the poly-Ig receptor (pIgR) and mucosal Ig transport.Eur J Immunol. 2021 Nov;51(11):2590-2606. doi: 10.1002/eji.202149383. Epub 2021 Sep 28. Eur J Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34411303 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Janeway CA, Jr, Medzhitov R. Innate immune recognition. Annu Rev Immunol. 2002;20:197–216. - PubMed
-
- Bork P, Holm L, Sander C. The immunoglobulin fold. Structural classification, sequence patterns and common core. J Mol Biol. 1994;242:309–320. - PubMed
-
- Harpaz Y, Chothia C. Many of the immunoglobulin superfamily domains in cell adhesion molecules and surface receptors belong to a new structural set which is close to that containing variable domains. J Mol Biol. 1994;238:528–539. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

