Landscape mapping of functional proteins in insulin signal transduction and insulin resistance: a network-based protein-protein interaction analysis
- PMID: 21305025
- PMCID: PMC3031563
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016388
Landscape mapping of functional proteins in insulin signal transduction and insulin resistance: a network-based protein-protein interaction analysis
Abstract
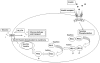
The type 2 diabetes has increased rapidly in recent years throughout the world. The insulin signal transduction mechanism gets disrupted sometimes and it's known as insulin-resistance. It is one of the primary causes associated with type-2 diabetes. The signaling mechanisms involved several proteins that include 7 major functional proteins such as INS, INSR, IRS1, IRS2, PIK3CA, Akt2, and GLUT4. Using these 7 principal proteins, multiple sequences alignment has been created. The scores between sequences also have been developed. We have constructed a phylogenetic tree and modified it with node and distance. Besides, we have generated sequence logos and ultimately developed the protein-protein interaction network. The small insulin signal transduction protein arrangement shows complex network between the functional proteins.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Neogi S. India, world diabetic capital. 2007. Hindustan Times, 3 September, www.hindustantimes.com/India-world-diabetes-capital/Article1-245889.
-
- Ginter E, Simko V. Diabetes type 2 pandemic in 21st century. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2010;111:134–7. - PubMed
-
- Kaufman FR. Type 2 diabetes mellitus in children and youth: a new epidemic. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2002;15:737–744. - PubMed
-
- Chakraborty C. Biochemical and molecular basis of insulin resistance. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2006;7:113–21. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

