Correlates of heavy drinking behaviors of Latino mothers and their adult daughters
- PMID: 21305910
- PMCID: PMC5636183
- DOI: 10.1080/02791072.2010.10400708
Correlates of heavy drinking behaviors of Latino mothers and their adult daughters
Abstract
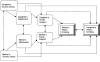
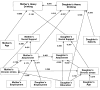
This study explored associations between adult Latina heavy drinking behaviors and potential psychosocial and demographic correlates. It used mother-daughter dyads and a cross-sectional design. Data were drawn from a community-based sample of 158 dyads of adult Latinas (n=316), age 18 years or older, recruited between 2004 and 2006. Bivariate and multivariate statistical methods, including logistic regression and pathway models, were used to analyze data. The study found that protective factors for heavy drinking behaviors for the mother included daughter's social support and mother's age, while for the daughter, they were mother's attachment and daughter's country of birth. Risk factors for daughter's heavy drinking behaviors were mother's social support and daughter's education. For both mother and daughter, chronic stress and drinking behavior associations were mediated by attachment and social support. Preventive interventions should target increasing levels of mother-daughter attachment and daughter's social support while decreasing stress levels for mothers and daughters.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Latina mother-daughter dyads: relations between attachment and sexual behavior under the influence of alcohol or drugs.Arch Sex Behav. 2010 Dec;39(6):1305-19. doi: 10.1007/s10508-009-9498-2. Epub 2009 Apr 28. Arch Sex Behav. 2010. PMID: 19399605 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of reproductive status changes on family functioning and well-being of mothers and daughters.J Early Adolesc. 1991 May;11(2):201-20. doi: 10.1177/0272431691112003. J Early Adolesc. 1991. PMID: 12285821
-
Exposure to cigarette smoke in utero: comparison of reports from mother and daughter.Epidemiology. 2008 Jul;19(4):628-33. doi: 10.1097/EDE.0b013e3181761cbd. Epidemiology. 2008. PMID: 18467961 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal influence on the sexual behavior of teen-age daughters.J Fam Issues. 1980 Mar;1(1):81-102. doi: 10.1177/0192513x8000100105. J Fam Issues. 1980. PMID: 12310348
-
The role of the mother-daughter relationship in explaining weight concern.Int J Eat Disord. 2000 Jul;28(1):78-83. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1098-108x(200007)28:1<78::aid-eat9>3.0.co;2-n. Int J Eat Disord. 2000. PMID: 10800016
Cited by
-
Improving Relational Functioning in Mother-Daughter Dyads With Obesity.Fam Community Health. 2023 Apr-Jun 01;46(2):103-111. doi: 10.1097/FCH.0000000000000359. Fam Community Health. 2023. PMID: 36799943 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Correlates of pro-drinking practices in drinking parents of adolescents in Hong Kong.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 18;10(3):e0119554. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119554. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25786105 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Armsden GC, Greenberg MT. The inventory of parent and peer attachment: Individual differences and their relationship to psychological well-being in adolescence. Journal of Youth and Adolescence. 1987;16:427–54. - PubMed
-
- Barrett AE, Turner RJ. Family structure and substance use in adolescence and early adulthood: Examining explanations for the relationship. Addiction. 2006;101:109–20. - PubMed
-
- Billings A, Moos R. Chronic and nonchronic unipolar depression: The differential role of environmental stressors and resources. Journal of Nervous and Mental Diseases. 1984;172:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Billings A, Cronkite R, Moos R. Social-environmental factors in unipolar depression: Comparisons of depressed patients and nondepressed controls. Journal of Abnormal Psychology. 1983;92:119–33. - PubMed
-
- Bogenschneider K. An ecological risk/protective theory for building prevention programs, policies, and community capacity to support youth. Family Relations. 1996;45:127–38.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
