Colchicine inhibits cationic dye uptake induced by ATP in P2X2 and P2X7 receptor-expressing cells: implications for its therapeutic action
- PMID: 21306580
- PMCID: PMC3130939
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01254.x
Colchicine inhibits cationic dye uptake induced by ATP in P2X2 and P2X7 receptor-expressing cells: implications for its therapeutic action
Abstract
Background and purpose: The two longest C-termini of the purinergic P2X receptors occur in the P2X2 and P2X7 receptors and are thought to interact with multiple cytoplasmic proteins, among which are members of the cytoskeleton, including microtubules. In this work we asked whether disrupting the microtubule cytoskeleton might affect the functions of these receptors.
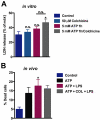
Experimental approach: Functions of heterologously expressed P2X2 and P2X7 receptors were evaluated with electrophysiology and dye uptake following ATP application. Permeabilization and secretion of pro-inflammatory agents were quantified from fresh or cultured peritoneal mouse macrophages, treated in vitro or in vivo with colchicine.
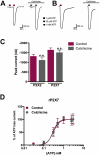
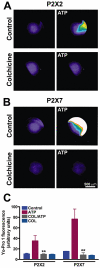
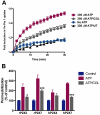
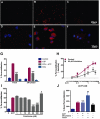
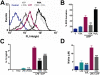
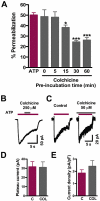
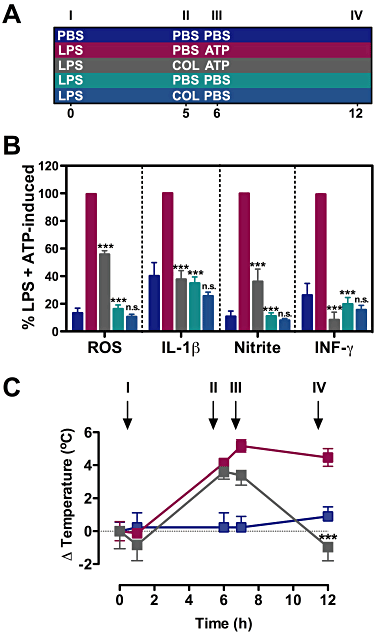
Key results: Disrupting the microtubule network with colchicine did not affect currents generated by ATP in P2X2 and P2X7 receptor-expressing cells but inhibited uptake of the dye Yo-Pro-1 in Xenopus oocytes and HEK293 cells expressing these channels. Peritoneal mouse macrophages showed less ATP-induced permeabilization to ethidium bromide in the presence of colchicine, and less reactive oxygen species (ROS) formation, nitric oxide (NO) and interleukin (IL)-1β release. Colchicine treatment did not affect ATP-evoked currents in macrophages. Finally, in vivo assays with mice inoculated with lipopolysaccharide and ATP showed diminished ROS, IL-1β, interferon-γ and NO production after colchicine treatment.
Conclusions and implications: Colchicine has known anti-inflammatory actions and is used to treat several conditions involving innate immunity, including gout and familial Mediterranean fever. Here we propose a new mechanism of action - inhibition of pore formation induced by activation of P2X receptors - which could explain some of the anti-inflammatory effects of colchicine.
© 2011 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology © 2011 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures
References
-
- Bezalel Y, Gershoni-Baruch R, Dagan E, Lidar M, Livneh A. The 3435T polymorphism in the ABCB1 gene and colchicine unresponsiveness in familial Mediterranean fever. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2009;27:S103–S104. - PubMed
-
- Brone B, Moechars D, Marrannes R, Mercken M, Meert T. P2X currents in peritoneal macrophages of wild type and P2X4 -/- mice. Immunol Lett. 2007;113:83–89. - PubMed
-
- Brough D, Rothwell NJ. Caspase-1-dependent processing of pro-interleukin-1beta is cytosolic and precedes cell death. J Cell Sci. 2007;120:772–781. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

