Epigenetic modification of hippocampal Bdnf DNA in adult rats in an animal model of post-traumatic stress disorder
- PMID: 21306736
- PMCID: PMC3335738
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2011.01.013
Epigenetic modification of hippocampal Bdnf DNA in adult rats in an animal model of post-traumatic stress disorder
Abstract
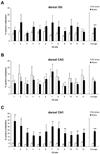
Epigenetic alterations of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (Bdnf) gene have been linked with memory, stress, and neuropsychiatric disorders. Here we examined whether there was a link between an established rat model of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and Bdnf DNA methylation. Adult male Sprague-Dawley rats were given psychosocial stress composed of two acute cat exposures in conjunction with 31 days of daily social instability. These manipulations have been shown previously to produce physiological and behavioral sequelae in rats that are comparable to symptoms observed in traumatized people with PTSD. We then assessed Bdnf DNA methylation patterns (at exon IV) and gene expression. We have found here that the psychosocial stress regimen significantly increased Bdnf DNA methylation in the dorsal hippocampus, with the most robust hypermethylation detected in the dorsal CA1 subregion. Conversely, the psychosocial stress regimen significantly decreased methylation in the ventral hippocampus (CA3). No changes in Bdnf DNA methylation were detected in the medial prefrontal cortex or basolateral amygdala. In addition, there were decreased levels of Bdnf mRNA in both the dorsal and ventral CA1. These results provide evidence that traumatic stress occurring in adulthood can induce CNS gene methylation, and specifically, support the hypothesis that epigenetic marking of the Bdnf gene may underlie hippocampal dysfunction in response to traumatic stress. Furthermore, this work provides support for the speculative notion that altered hippocampal Bdnf DNA methylation is a cellular mechanism underlying the persistent cognitive deficits which are prominent features of the pathophysiology of PTSD.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Involvement of dysregulated hippocampal histone H3K9 methylation at the promoter of the BDNF gene in impaired memory extinction.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2024 Nov;241(11):2363-2374. doi: 10.1007/s00213-024-06640-7. Epub 2024 Jun 28. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2024. PMID: 38940908 Free PMC article.
-
The cognitive impairment induced by zinc deficiency in rats aged 0∼2 months related to BDNF DNA methylation changes in the hippocampus.Nutr Neurosci. 2017 Nov;20(9):519-525. doi: 10.1080/1028415X.2016.1194554. Epub 2016 Jun 22. Nutr Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 27329329
-
Enhanced hippocampal BDNF/TrkB signaling in response to fear conditioning in an animal model of posttraumatic stress disorder.J Psychiatr Res. 2011 Apr;45(4):460-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2010.08.009. Epub 2010 Sep 21. J Psychiatr Res. 2011. PMID: 20863519
-
Possible Reversal of PTSD-Related DNA Methylation by Sympathetic Blockade.J Mol Neurosci. 2017 May;62(1):67-72. doi: 10.1007/s12031-017-0911-3. Epub 2017 Mar 31. J Mol Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28364364 Review.
-
The Relationships Between Stress, Mental Disorders, and Epigenetic Regulation of BDNF.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 18;21(4):1375. doi: 10.3390/ijms21041375. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32085670 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Long-lasting regulation of hippocampal Bdnf gene transcription after contextual fear conditioning.Genes Brain Behav. 2012 Aug;11(6):651-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-183X.2012.00805.x. Epub 2012 May 30. Genes Brain Behav. 2012. PMID: 22574690 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring epigenetic regulation of fear memory and biomarkers associated with post-traumatic stress disorder.Front Psychiatry. 2013 Jul 1;4:62. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2013.00062. eCollection 2013. Front Psychiatry. 2013. PMID: 23847551 Free PMC article.
-
Contrasting hippocampal and amygdalar expression of genes related to neural plasticity during escape from social aggression.Physiol Behav. 2012 Dec 5;107(5):670-9. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2012.03.005. Epub 2012 Mar 16. Physiol Behav. 2012. PMID: 22450262 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Approach to PTSD: In the Aspects of Rat Models.Glob Med Genet. 2021 Nov 11;9(1):7-13. doi: 10.1055/s-0041-1736633. eCollection 2022 Mar. Glob Med Genet. 2021. PMID: 35169777 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Myocardial hypersensitivity to ischemic injury is not reversed by clonidine or propranolol in a predator-based rat model of posttraumatic stress disorder.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2019 Mar 8;89:117-124. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2018.09.003. Epub 2018 Sep 5. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 30194949 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adamec RE, Blundell J, Burton P. Neural circuit changes mediating lasting brain and behavioral response to predator stress. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews. 2005;29:1225–1241. - PubMed
-
- Afifi TO, Asmundson GJG, Taylor S, Jang KL. The role of genes and environment on trauma exposure and posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms: A review of twin studies. Clinical Psychology Review. 2010;30:101–112. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagonistic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-IV. Washington DC: American Psychiatric Association; 1994.
-
- Andrews B, Brewin CR, Rose S. Gender, social support, and PTSD in victims of violent crime. Journal of Traumatic Stress. 2003;16:421–427. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

