Comparison of the DiversiLab repetitive element PCR system with spa typing and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis for clonal characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 21307215
- PMCID: PMC3122836
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.02254-10
Comparison of the DiversiLab repetitive element PCR system with spa typing and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis for clonal characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
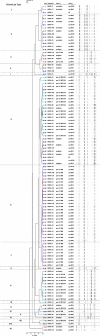
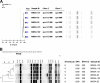
The emergence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) has become an increasing problem worldwide in recent decades. Molecular typing methods have been developed to identify clonality of strains and monitor spread of MRSA. We compared a new commercially available DiversiLab (DL) repetitive element PCR system with spa typing, spa clonal cluster analysis, and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) in terms of discriminatory power and concordance. A collection of 106 well-defined MRSA strains from our hospital was analyzed, isolated between 1994 and 2006. In addition, we analyzed 6 USA300 strains collected in our institution. DL typing separated the 106 MRSA isolates in 10 distinct clusters and 8 singleton patterns. Clustering analysis into spa clonal complexes resulted in 3 clusters: spa-CC 067/548, spa-CC 008, and spa-CC 012. The discriminatory powers (Simpson's index of diversity) were 0.982, 0.950, 0.846, and 0.757 for PFGE, spa typing, DL typing, and spa clonal clustering, respectively. DL typing and spa clonal clustering showed the highest concordance, calculated by adjusted Rand's coefficients. The 6 USA300 isolates grouped homogeneously into distinct PFGE and DL clusters, and all belonged to spa type t008 and spa-CC 008. Among the three methods, DL proved to be rapid and easy to perform. DL typing qualifies for initial screening during outbreak investigation. However, compared to PFGE and spa typing, DL typing has limited discriminatory power and therefore should be complemented by more discriminative methods in isolates that share identical DL patterns.
Figures

References
-
- Church D. L., Chow B. L., Lloyd T., Gregson D. B. 2011. Comparison of automated repetitive-sequence-based polymerase chain reaction and spa typing versus pulsed-field gel electrophoresis for molecular typing of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 69:30–37 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

