Synchronization of presynaptic input to motor units of tongue, inspiratory intercostal, and diaphragm muscles
- PMID: 21307319
- PMCID: PMC3094165
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.01078.2010
Synchronization of presynaptic input to motor units of tongue, inspiratory intercostal, and diaphragm muscles
Abstract
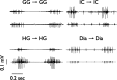
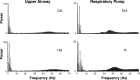
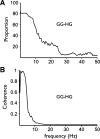
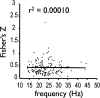
The respiratory central pattern generator distributes rhythmic excitatory input to phrenic, intercostal, and hypoglossal premotor neurons. The degree to which this input shapes motor neuron activity can vary across respiratory muscles and motor neuron pools. We evaluated the extent to which respiratory drive synchronizes the activation of motor unit pairs in tongue (genioglossus, hyoglossus) and chest-wall (diaphragm, external intercostals) muscles using coherence analysis. This is a frequency domain technique, which characterizes the frequency and relative strength of neural inputs that are common to each of the recorded motor units. We also examined coherence across the two tongue muscles, as our previous work shows that, despite being antagonists, they are strongly coactivated during the inspiratory phase, suggesting that excitatory input from the premotor neurons is distributed broadly throughout the hypoglossal motoneuron pool. All motor unit pairs showed highly correlated activity in the low-frequency range (1-8 Hz), reflecting the fundamental respiratory frequency and its harmonics. Coherence of motor unit pairs recorded either within or across the tongue muscles was similar, consistent with broadly distributed premotor input to the hypoglossal motoneuron pool. Interestingly, motor units from diaphragm and external intercostal muscles showed significantly higher coherence across the 10-20-Hz bandwidth than tongue-muscle units. We propose that the lower coherence in tongue-muscle motor units over this range reflects a larger constellation of presynaptic inputs, which collectively lead to a reduction in the coherence between hypoglossal motoneurons in this frequency band. This, in turn, may reflect the relative simplicity of the respiratory drive to the diaphragm and intercostal muscles, compared with the greater diversity of functions fulfilled by muscles of the tongue.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The neural control of human inspiratory muscles.Prog Brain Res. 2014;209:295-308. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-63274-6.00015-1. Prog Brain Res. 2014. PMID: 24746054 Review.
-
Differential activation among five human inspiratory motoneuron pools during tidal breathing.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2007 Feb;102(2):772-80. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00683.2006. Epub 2006 Oct 19. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2007. PMID: 17053105
-
Glutamatergic input varies with phrenic motor neuron size.J Neurophysiol. 2019 Oct 1;122(4):1518-1529. doi: 10.1152/jn.00430.2019. Epub 2019 Aug 7. J Neurophysiol. 2019. PMID: 31389739 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of pulmonary stretch receptor feedback and CO(2) on upper airway and respiratory pump muscle activity in the rat.J Physiol. 2001 Apr 15;532(Pt 2):525-34. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.0525f.x. J Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11306669 Free PMC article.
-
Neural control of human inspiratory muscles. What have we learnt from the study of single motor units?J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2025 Aug;83:103026. doi: 10.1016/j.jelekin.2025.103026. Epub 2025 Jun 10. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2025. PMID: 40570773 Review.
Cited by
-
Respiration-related discharge of hyoglossus muscle motor units in the rat.J Neurophysiol. 2014 Jan;111(2):361-8. doi: 10.1152/jn.00670.2013. Epub 2013 Oct 16. J Neurophysiol. 2014. PMID: 24133219 Free PMC article.
-
Anatomic connections of the diaphragm: influence of respiration on the body system.J Multidiscip Healthc. 2013 Jul 25;6:281-91. doi: 10.2147/JMDH.S45443. Print 2013. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2013. PMID: 23940419 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental Nicotine Exposure Alters Synaptic Input to Hypoglossal Motoneurons and Is Associated with Altered Function of Upper Airway Muscles.eNeuro. 2019 Nov 15;6(6):ENEURO.0299-19.2019. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0299-19.2019. Print 2019 Nov/Dec. eNeuro. 2019. PMID: 31712219 Free PMC article.
-
Crossed motor innervation of the base of human tongue.J Neurophysiol. 2015 Jun 1;113(10):3499-510. doi: 10.1152/jn.00051.2015. Epub 2015 Apr 8. J Neurophysiol. 2015. PMID: 25855691 Free PMC article.
-
Respiratory related control of hypoglossal motoneurons--knowing what we do not know.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2011 Oct 15;179(1):43-7. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2011.06.023. Epub 2011 Jul 2. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2011. PMID: 21741499 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amjad AM, Breeze P, Conway BA, Halliday DM, Rosenberg JR. A framework for the analysis of neuronal networks. Prog Brain Res 80: 243–255; discussion 239–242, 1989. - PubMed
-
- Bailey EF, Fregosi RF. Coordination of intrinsic and extrinsic tongue muscles during spontaneous breathing in the rat. J Appl Physiol 96: 440–449, 2004. - PubMed
-
- Bailey EF, Fregosi RF. Modulation of upper airway muscle activities by bronchopulmonary afferents. J Appl Physiol 101: 609–617, 2006. - PubMed
-
- Bailey EF, Huang Y, Fregosi RF. The anatomic consequences of intrinsic tongue muscle activation. J Appl Physiol 101: 1377–1385, 2006. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

