Mouse models of hepatocarcinogenesis: what can we learn for the prevention of human hepatocellular carcinoma?
- PMID: 21307402
- PMCID: PMC3157729
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.170
Mouse models of hepatocarcinogenesis: what can we learn for the prevention of human hepatocellular carcinoma?
Abstract
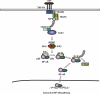
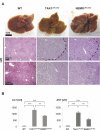
There is growing evidence that chronic inflammatory processes are involved in triggering the sequence from chronic liver injury to liver fibrosis, ultimately leading to liver cancer. In the last years this process has been recapitulated in a growing number of different mouse models. However, it has remained unclear whether and how these mouse models reflect the clinical reality of human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Research with animal models but also human liver specimens has indicated that the NF-κB signaling pathway might withhold a crucial function in the mediation of chronic hepatic inflammation and the transition to HCC in humans. However, previous studies led to divergent and partly conflicting results with regards to the functional role of NF-κB in hepatocarcinogenesis. Here, we discuss a new genetic mouse model for HCC, the liver-specific TAK1 knockout mouse, which lacks the NF-κB activating kinase TAK1 specifically in parenchymal liver cells. Molecular findings in this mouse model and their possible significance for chemopreventive strategies against HCC are compared to other murine HCC models.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Chuang SC, La Vecchia C, Boffetta P. Liver cancer: descriptive epidemiology and risk factors other than HBV and HCV infection. Cancer Lett. 2009;286:9–14. - PubMed
-
- Cabibbo G, Craxi A. Epidemiology, risk factors and surveillance of hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2010;14:352–355. - PubMed
-
- Sherman M. Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncology. 2010;78(Suppl 1):7–10. - PubMed
-
- Sherman M. Hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiology, surveillance, and diagnosis. Semin Liver Dis. 2010;30:3–16. - PubMed
-
- Cheng AL, Kang YK, Chen Z, Tsao CJ, Qin S, Kim JS, Luo R, et al. Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10:25–34. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

