Targeting NFĸB mediated breast cancer chemoresistance through selective inhibition of sphingosine kinase-2
- PMID: 21307639
- PMCID: PMC3084971
- DOI: 10.4161/cbt.11.7.14903
Targeting NFĸB mediated breast cancer chemoresistance through selective inhibition of sphingosine kinase-2
Abstract
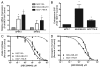
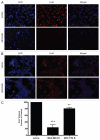
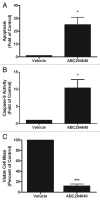
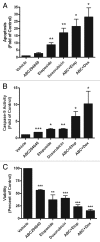
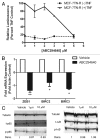
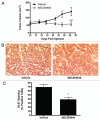
Resistance to chemotherapy remains a significant obstacle in the treatment of hormone- independent breast cancer. Recent evidence suggests that altered sphingolipid signaling through increased sphingosine kinase activity may be an important mediator of breast cancer drug resistance. Sphingosine kinase-1 (Sphk1) is a proposed key regulator of breast cancer tumorigenesis, proliferation and resistance. There is, however, conflicting data on the role of sphingosine kinase-2 (Sphk2) in cancer biology and resistance, with some suggesting that Sphk2 has an opposing role to that of Sphk1. Here, we studied the effects of the novel selective Sphk2 inhibitor, ABC294640 (3-(4-chlorophenyl)-adamantane-1-carboxylic acid (pyridin-4-ylmethyl) amide), on human breast cancer. ABC294640 blocked both viability and survival at low micromolar IC(50) concentrations in the endocrine therapy-resistant MDA-MB-231 and chemoresistant MCF-7TN-R cell systems. Treatment with the inhibitor significantly reduced proliferation, as seen in immunofluorescence staining of Ki-67 in vitro. Interestingly, pharmacological inhibition of Sphk2 induced apoptosis through the intrinsic programmed cell death pathway. Furthermore, ABC294640 also diminished NF-ĸB survival signaling, through decreased activation of the Ser536 phosphorylation site on the p65 subunit. Xenografts of MCF-7TN-R cells growing in immunocompromised mice were utilized to validate the therapeutic efficacy of the sphingosine kinase-2 inhibitor. Treatment with 50 mg of ABC294640/kg completely blocked tumor volume in this model. These results indicate that pharmacological inhibition of Sphk2 with the orally bioavailable selective inhibitor, ABC294640, has therapeutic potential in the treatment of chemo- and endocrine therapy- resistant breast cancer.
Figures
References
-
- Meacham WD, Antoon JW, Burow ME, Struckhoff AP, Beckman BS. Sphingolipids as determinants of apoptosis and chemoresistance in the MCF-7 cell model system. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 2009;234:1253–1263. - PubMed
-
- Sukocheva O, Wang L, Verrier E, Vadas MA, Xia P. Restoring endocrine response in breast cancer cells by inhibition of the sphingosine kinase-1 signaling pathway. Endocrinology. 2009;150:4484–4492. - PubMed
-
- Cuvillier O, Pirianov G, Kleuser B, Vanek PG, Coso OA, Gutkind S, et al. Suppression of ceramide-mediated programmed cell death by sphingosine-1-phosphate. Nature. 1996;381:800–803. - PubMed
-
- French KJ, Schrecengost RS, Lee BD, Zhuang Y, Smith SN, Eberly JL, et al. Discovery and evaluation of inhibitors of human sphingosine kinase. Cancer Res. 2003;63:5962–5969. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
