Improved performance of urinary biomarkers of acute kidney injury in the critically ill by stratification for injury duration and baseline renal function
- PMID: 21307838
- PMCID: PMC3884688
- DOI: 10.1038/ki.2010.555
Improved performance of urinary biomarkers of acute kidney injury in the critically ill by stratification for injury duration and baseline renal function
Abstract
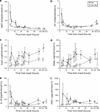
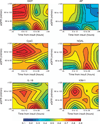
To better understand the diagnostic and predictive performance of urinary biomarkers of kidney injury, we evaluated γ-glutamyltranspeptidase (GGT), alkaline phosphatase (AP), neutrophil-gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL), cystatin C (CysC), kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1), and interleukin-18 (IL-18) in a prospective observational study of 529 patients in 2 general intensive care units (ICUs). Comparisons were made using the area under the receiver operator characteristic curve (AUC) for diagnosis or prediction of acute kidney injury (AKI), dialysis, or death, and reassessed after patient stratification by baseline renal function (estimated glomerular filtration rate, eGFR) and time after renal insult. On ICU entry, no biomarker had an AUC above 0.7 in the diagnosis or prediction of AKI. Several biomarkers (NGAL, CysC, and IL-18) predicted dialysis (AUC over 0.7), and all except KIM-1 predicted death at 7 days (AUC between 0.61 and 0.69). Performance was improved by stratification for eGFR or time or both. With eGFR <60 ml/min, CysC and KIM-1 had AUCs of 0.69 and 0.73, respectively, within 6 h of injury, and between 12 and 36 h, CysC (0.88), NGAL (0.85), and IL-18 (0.94) had utility. With eGFR >60 ml/min, GGT (0.73), CysC (0.68), and NGAL (0.68) had the highest AUCs within 6 h of injury, and between 6 and 12 h, all AUCs except AP were between 0.68 and 0.78. Beyond 12 h, NGAL (0.71) and KIM-1 (0.66) performed best. Thus, the duration of injury and baseline renal function should be considered in evaluating biomarker performance to diagnose AKI.
Figures

Comment in
-
How to use biomarkers efficiently in acute kidney injury.Kidney Int. 2011 May;79(10):1047-50. doi: 10.1038/ki.2011.21. Kidney Int. 2011. PMID: 21527944
References
-
- Han WK, Bailly V, Abichandani R, et al. Kidney Injury Molecule-1 (KIM-1): a novel biomarker for human renal proximal tubule injury. Kidney Int. 2002;62:237–244. - PubMed
-
- Westhuyzen J, Endre ZH, Reece G, et al. Measurement of tubular enzymuria facilitates early detection of acute renal impairment in the intensive care unit. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2003;18:543–551. - PubMed
-
- Parikh CR, Abraham E, Ancukiewicz M, et al. Urine IL-18 is an early diagnostic marker for acute kidney injury and predicts mortality in the intensive care unit. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005;16:3046–3052. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

