HDAC inhibition in rheumatoid arthritis and juvenile idiopathic arthritis
- PMID: 21308151
- PMCID: PMC3105145
- DOI: 10.2119/molmed.2011.00030
HDAC inhibition in rheumatoid arthritis and juvenile idiopathic arthritis
Abstract
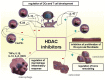
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) are heterogeneous autoimmune diseases characterized by chronic joint inflammation. Methotrexate is used as the gold standard to treat rheumatoid arthritis, yet there are many patients in whom the disease cannot be controlled or who experience unacceptable intolerance. Most of the biologics currently used are effective, but mostly if combined with methotrexate. Long-term possible side effects, such as impaired host defense mechanisms against infection and lymphoma, are distinct disadvantages and a major concern of anticytokine therapies. Parenteral administration is a problem, particularly in children. Thus, there is a need to explore new treatment options. Here we review the properties of histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi) as they apply to rheumatoid arthritis by looking at effects on cytokine production, T-cell differentiation and the function of macrophages, dendritic cells, osteoblasts, osteoclasts and synovial fibroblasts. We also review the safety and efficacy of givinostat (ITF 2357) in the treatment of systemic onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis (SOJIA) and its influence on the cytokine networks in SOJIA. Givinostat is an orally active HDACi which was given to children with SOJIA. After 12 wk of treatment, there were significant benefits, particularly in reducing the pain and arthritic component of the disease and decreasing the neutrophilia. CD40L, IL-1α and IFNγ in whole blood lysates decreased at wks 2 and 4 compared with baseline levels. The clinical data are consistent with those from animal models of rheumatoid arthritis and suggest that trials with HDACi are promising as a safe oral alternative to anticytokines and methotrexate.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00570661.
Figures
References
-
- Imboden JB. The immunopathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Annu Rev Pathol. 2009;4:417–34. - PubMed
-
- Choy EH, Panayi GS. Cytokine pathways and joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:907–16. - PubMed
-
- Petty RE, et al. International League of Associations for Rheumatology classification of juvenile idiopathic arthritis: second revision, Edmonton, 2001. J Rheumatol. 2004;31:390–92. - PubMed
-
- Li X, et al. The role of interleukin-17 in mediating joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;397:131–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

