Treatment with paracetamol, ketorolac or etoricoxib did not hinder alveolar bone healing: a histometric study in rats
- PMID: 21308296
- PMCID: PMC3881766
- DOI: 10.1590/s1678-77572010000600016
Treatment with paracetamol, ketorolac or etoricoxib did not hinder alveolar bone healing: a histometric study in rats
Abstract
Prostaglandins control osteoblastic and osteoclastic function under physiological or pathological conditions and are important modulators of the bone healing process. The non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) inhibit cyclooxygenase (COX) activity and consequently prostaglandins synthesis. Experimental and clinical evidence has indicated a risk for reparative bone formation related to the use of non-selective (COX-1 and COX-2) and COX-2 selective NSAIDs. Ketorolac is a non-selective NSAID which, at low doses, has a preferential COX-1 inhibitory effect and etoricoxib is a new selective COX-2 inhibitor. Although literature data have suggested that ketorolac can interfere negatively with long bone fracture healing, there seems to be no study associating etoricoxib with reparative bone formation. Paracetamol/acetaminophen, one of the first choices for pain control in clinical dentistry, has been considered a weak anti-inflammatory drug, although supposedly capable of inhibiting COX-2 activity in inflammatory sites.
Objective: The purpose of the present study was to investigate whether paracetamol, ketorolac and etoricoxib can hinder alveolar bone formation, taking the filling of rat extraction socket with newly formed bone as experimental model.
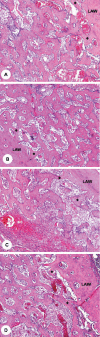
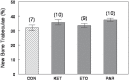
Material and methods: The degree of new bone formation inside the alveolar socket was estimated two weeks after tooth extraction by a differential point-counting method, using an optical microscopy with a digital camera for image capture and histometry software. Differences between groups were analyzed by ANOVA after confirming a normal distribution of sample data.
Results and conclusions: Histometric results confirmed that none of the tested drugs had a detrimental effect in the volume fraction of bone trabeculae formed inside the alveolar socket.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differential inhibition of fracture healing by non-selective and cyclooxygenase-2 selective non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.J Orthop Res. 2003 Jul;21(4):670-5. doi: 10.1016/S0736-0266(03)00003-2. J Orthop Res. 2003. PMID: 12798067
-
[Case report: reversible acute renal failure following therapy with both ketorolac (non-selective non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug NSAID) and celecoxib (COX-2 selective) in the same patient].G Ital Nefrol. 2002 Mar-Apr;19(2):199-203. G Ital Nefrol. 2002. PMID: 12195419 Italian.
-
Upregulation of intrinsic apoptotic pathway in NSAIDs mediated chemoprevention of experimental lung carcinogenesis.Pharmacol Rep. 2012;64(3):615-24. doi: 10.1016/s1734-1140(12)70857-5. Pharmacol Rep. 2012. PMID: 22814015
-
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, cyclooxygenase-2 and the bone healing process.Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2008 Jan;102(1):10-4. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-7843.2007.00149.x. Epub 2007 Oct 31. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2008. PMID: 17973900 Review.
-
The modern pharmacology of paracetamol: therapeutic actions, mechanism of action, metabolism, toxicity and recent pharmacological findings.Inflammopharmacology. 2013 Jun;21(3):201-32. doi: 10.1007/s10787-013-0172-x. Epub 2013 May 30. Inflammopharmacology. 2013. PMID: 23719833 Review.
Cited by
-
Ketorolac administration does not delay early fracture healing in a juvenile rat model: a pilot study.J Pediatr Orthop. 2013 Jun;33(4):415-21. doi: 10.1097/BPO.0b013e318288b46f. J Pediatr Orthop. 2013. PMID: 23653032 Free PMC article.
-
Pulp response of rats submitted to bleaching and the use of different anti-inflammatory drugs.PLoS One. 2019 Jan 8;14(1):e0210338. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0210338. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30620760 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of the Highly COX-2-Selective Analgesic NSAID Etoricoxib on Human Periodontal Ligament Fibroblasts during Compressive Orthodontic Mechanical Strain.Mediators Inflamm. 2019 Mar 10;2019:2514956. doi: 10.1155/2019/2514956. eCollection 2019. Mediators Inflamm. 2019. PMID: 30983880 Free PMC article.
-
The Influence of Different Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs on Alveolar Bone in Rats: An Experimental Study.Acta Stomatol Croat. 2015 Dec;49(4):325-30. doi: 10.15644/asc49/4/8. Acta Stomatol Croat. 2015. PMID: 27688417 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Pain and Analgesia on Orthopedic and Wound-healing Models in Rats and Mice.Comp Med. 2019 Dec 1;69(6):535-545. doi: 10.30802/AALAS-CM-19-000013. Epub 2019 Sep 27. Comp Med. 2019. PMID: 31561753 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Azoubel MC, Menezes AM, Bezerra D, Oriá RB, Ribeiro RA, Brito GA. Comparison of etoricoxib and indomethacin for the treatment of experimental periodontitis in rats. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2007;40:117–125. - PubMed
-
- Baratieri A, Deli R. The effect on bone repair of aspirin cones placed in extraction sockets in dogs: a histopathologic study. J Oral Pathol. 1979;8:198–206. - PubMed
-
- Battisti N. The evaluation of the analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects of flurbiprofen mouthwash and 100-mg tablets in oral medicine. Minerva Stomatol. 1994;43:141–144. - PubMed
-
- Bailey BM, Zaki G, Rotman H, Woodwards R. A double-blind comparative study of soluble aspirin and diclofenac dispersible in the control of postextraction pain after removal of impacted third molars. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1993;22:238–241. - PubMed
-
- Bergenstock M, Min W, Simon AM, Sabatino C, O'Connor JP A comparison between the effects of acetaminophen and celecoxib on bone fracture healing in rats. J Orthop Trauma. 2005;19:717–723. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

