Megakaryocyte lineage-specific class VI β-tubulin suppresses microtubule dynamics, fragments microtubules, and blocks cell division
- PMID: 21309084
- PMCID: PMC3082363
- DOI: 10.1002/cm.20503
Megakaryocyte lineage-specific class VI β-tubulin suppresses microtubule dynamics, fragments microtubules, and blocks cell division
Abstract
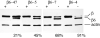
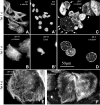
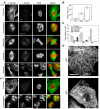
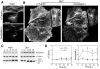
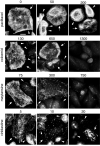
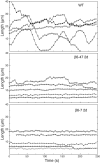
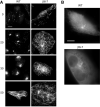
Class VI β-tubulin (β6) is the most divergent tubulin produced in mammals and is found only in platelets and mature megakaryocytes. To determine how this unique tubulin isotype affects microtubule assembly and organization, we expressed the cDNA in tissue culture cells under the control of a tetracycline regulated promoter. The β6 coassembled with other endogenous β-tubulin isotypes into a normal microtubule array; but once the cells entered mitosis it caused extensive fragmentation of the microtubules, disrupted the formation of the spindle apparatus, and allowed entry into G1 phase without cytokinesis to produce large multinucleated cells. The microtubule fragments persisted into subsequent cell cycles and accumulated around the membrane in a marginal band-like appearance. The persistence of the fragments could be traced to a pronounced suppression of microtubule dynamic instability. Impairment of centrosomal nucleation also contributed to the loss of a normal microtubule cytoskeleton. Incorporation of β6 allowed microtubules to resist the effects of colcemid and maytansine, but not vinblastine or paclitaxel; however, cellular resistance to colcemid or maytansine did not occur because expression of β6 prevented cell division. The results indicate that many of the morphological features of megakaryocyte differentiation can be recapitulated in non-hematopoietic cells by β6 expression and they provide a mechanistic basis for understanding these changes.
Copyright © 2011 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Ahmad S, Singh B, Gupta RS. Nucleotide sequences of three different isoforms of beta-tubulin cDNA from Chinese hamster ovary cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991;1090:252–254. - PubMed
-
- Akhmanova A, Steinmetz MO. Tracking the ends: a dynamic protein network controls the fate of microtubule tips. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9:309–322. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

