Beyond the endoplasmic reticulum: atypical GRP78 in cell viability, signalling and therapeutic targeting
- PMID: 21309747
- PMCID: PMC3353658
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20101569
Beyond the endoplasmic reticulum: atypical GRP78 in cell viability, signalling and therapeutic targeting
Abstract
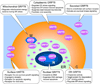
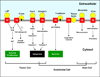
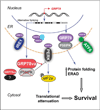
GRP78 (glucose-regulated protein of 78 kDa) is traditionally regarded as a major ER (endoplasmic reticulum) chaperone facilitating protein folding and assembly, protein quality control, Ca(2+) binding and regulating ER stress signalling. It is a potent anti-apoptotic protein and plays a critical role in tumour cell survival, tumour progression and angiogenesis, metastasis and resistance to therapy. Recent evidence shows that GRP78 can also exist outside the ER. The finding that GRP78 is present on the surface of cancer but not normal cells in vivo represents a paradigm shift on how GRP78 controls cell homoeostasis and provides an opportunity for cancer-specific targeting. Cell-surface GRP78 has emerged as an important regulator of tumour cell signalling and viability as it forms complexes with a rapidly expanding repertoire of cell-surface protein partners, regulating proliferation, PI3K (phosphoinositide 3-kinase)/Akt signalling and cell viability. Evidence is also emerging that GRP78 serves as a receptor for viral entry into host cells. Additionally, a novel cytosolic form of GRP78 has been discovered prominently in leukaemia cells. These, coupled with reports of nucleus- and mitochondria-localized forms of GRP78, point to the previously unanticipated role of GRP78 beyond the ER that may be critical for cell viability and therapeutic targeting.
© The Authors Journal compilation © 2011 Biochemical Society
Figures
References
-
- Ting J, Lee AS. Human gene encoding the 78,000-dalton glucose-regulated protein and its pseudogene: structure, conservation, and regulation. DNA. 1988;7:275–286. - PubMed
-
- Lee AS. The glucose-regulated proteins: stress induction and clinical applications. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2001;26:504–510. - PubMed
-
- Lee AS. GRP78 induction in cancer: therapeutic and prognostic implications. Cancer Res. 2007;67:3496–3499. - PubMed
-
- Gonzalez-Gronow M, Selim MA, Papalas J, Pizzo SV. GRP78: a multifunctional receptor on the cell surface. Antioxid. Redox. Signal. 2009;11:2299–2306. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

