Unifying cancer genetics
- PMID: 21311342
- PMCID: PMC3412587
- DOI: 10.1097/GIM.0b013e31820d5e87
Unifying cancer genetics
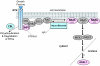
Figures
References
-
- Rushlow D, Piovesan B, Zhang K, et al. Detection of mosaic RB1 mutations in families with retinoblastoma. Hum Mutat. 2009;30:842–851. - PubMed
-
- Armengol C, Cairo S, Fabre M, Buendia MA. Wnt signaling and hepatocarcinogenesis: The hepatoblastoma model. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009 - PubMed
-
- Lopez-Terrada D, Gunaratne PH, Adesina AM, et al. Histologic subtypes of hepatoblastoma are characterized by differential canonical Wnt and Notch pathway activation in DLK+ precursors. Hum Pathol. 2009;40:783–794. - PubMed
-
- Aretz S, Koch A, Uhlhaas S, et al. Should children at risk for familial adenomatous polyposis be screened for hepatoblastoma and children with apparently sporadic hepatoblastoma be screened for APC germline mutations? Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2006;47:811–818. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

