The comparison of a technology-based system and an in-person behavioral weight loss intervention
- PMID: 21311506
- PMCID: PMC3753800
- DOI: 10.1038/oby.2011.13
The comparison of a technology-based system and an in-person behavioral weight loss intervention
Abstract
The purpose of this study was to compare a technology-based system, an in-person behavioral weight loss intervention, and a combination of both over a 6-month period in overweight adults. Fifty-one subjects (age: 44.2 ± 8.7 years, BMI: 33.7 ± 3.6 kg/m(2)) participated in a 6-month behavioral weight loss program and were randomized to one of three groups: standard behavioral weight loss (SBWL), SBWL plus technology-based system (SBWL+TECH), or technology-based system only (TECH). All groups reduced caloric intake and progressively increased moderate intensity physical activity. SBWL and SBWL+TECH attended weekly meetings. SBWL+TECH also received a TECH that included an energy monitoring armband and website to monitor energy intake and expenditure. TECH used the technology system and received monthly telephone calls. Body weight and physical activity were assessed at 0 and 6 months. Retention at 6 months was significantly different (P = 0.005) between groups (SBWL: 53%, SBWL+TECH: 100%, and TECH: 77%). Intent-to-treat (ITT) analysis revealed significant weight losses at 6 months in SBWL+TECH (-8.8 ± 5.0 kg, -8.7 ± 4.7%), SBWL (-3.7 ± 5.7 kg, -4.1 ± 6.3%), and TECH (-5.8 ± 6.6 kg, -6.3 ± 7.1%) (P < 0.001). Self-report physical activity increased significantly in SBWL (473.9 ± 800.7 kcal/week), SBWL+TECH (713.9 ± 1,278.8 kcal/week), and TECH (1,066.2 ± 1,371 kcal/week) (P < 0.001), with no differences between groups (P = 0.25). The TECH used in conjunction with monthly telephone calls, produced similar, if not greater weight losses and changes in physical activity than the standard in-person behavioral program at 6 months. The use of this technology may provide an effective short-term clinical alternative to standard in-person behavioral weight loss interventions, with the longer term effects warranting investigation.
Figures
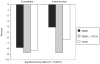
References
-
- Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Ogden CL, Curtin LR. Prevalence and trends in obesity among US adults, 1999-2008. JAMA. 2010;303:235–241. - PubMed
-
- Manson JE, Willett WC, Stampfer MJ, et al. Body weight and mortality among women. N Engl J Med. 1995;333:677–685. - PubMed
-
- Field AE, Coakley EH, Must A, et al. Impact of overweight on the risk of developing common chronic diseases during a 10-year period. Arch Intern Med. 2001;161:1581–1586. - PubMed
-
- Wilson PW, D'Agostino RB, Sullivan L, Parise H, Kannel WB. Overweight and obesity as determinants of cardiovascular risk: the Framingham experience. Arch Intern Med. 2002;162:1867–1872. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

