Argininosuccinate lyase deficiency-argininosuccinic aciduria and beyond
- PMID: 21312326
- PMCID: PMC3073162
- DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.c.30289
Argininosuccinate lyase deficiency-argininosuccinic aciduria and beyond
Abstract
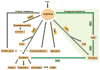
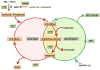
The urea cycle consists of six consecutive enzymatic reactions that convert waste nitrogen into urea. Deficiencies of any of these enzymes of the cycle result in urea cycle disorders (UCD), a group of inborn errors of hepatic metabolism that often result in life threatening hyperammonemia. Argininosuccinate lyase (ASL) is a cytosolic enzyme which catalyzes the fourth reaction in the cycle and the first degradative step, that is, the breakdown of argininosuccinic acid to arginine and fumarate. Deficiency of ASL results in an accumulation of argininosuccinic acid in tissues, and excretion of argininosuccinic acid in urine leading to the condition argininosuccinic aciduria (ASA). ASA is an autosomal recessive disorder and is the second most common UCD. In addition to the accumulation of argininosuccinic acid, ASL deficiency results in decreased synthesis of arginine, a feature common to all UCDs except argininemia. Arginine is not only the precursor for the synthesis of urea and ornithine as part of the urea cycle but it is also the substrate for the synthesis of nitric oxide, polyamines, proline, glutamate, creatine, and agmatine. Hence, while ASL is the only enzyme in the body able to generate arginine, at least four enzymes use arginine as substrate: arginine decarboxylase, arginase, nitric oxide synthetase (NOS) and arginine/glycine aminotransferase. In the liver, the main function of ASL is ureagenesis, and hence, there is no net synthesis of arginine. In contrast, in most other tissues, its role is to generate arginine that is designated for the specific cell's needs. While patients with ASA share the acute clinical phenotype of hyperammonemia, encephalopathy, and respiratory alkalosis common to other UCD, they also present with unique chronic complications most probably caused by a combination of tissue specific deficiency of arginine and/or elevation of argininosuccinic acid. This review article summarizes the clinical characterization, biochemical, enzymatic, and molecular features of this disorder. Current treatment, prenatal diagnosis, diagnosis through the newborn screening as well as hypothesis driven future treatment modalities are discussed.
Copyright © 2011 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Consensus statement from a conference for the management of patients with urea cycle disorders. J Pediatr. 138(1 Suppl):S1–5. - PubMed
-
- Allan JD, Cusworth DC, Dent CE, Wilson VK. A disease, probably hereditary characterised by severe mental deficiency and a constant gross abnormality of aminoacid metabolism. Lancet. 1958;1(7013):182–187. - PubMed
-
- Aoyagi K. Inhibition of arginine synthesis by urea: a mechanism for arginine deficiency in renal failure which leads to increased hydroxyl radical generation. Mol Cell Biochem. 2003;244(1–2):11–15. - PubMed
-
- Aoyagi K, Shahrzad S, Iida S, Tomida C, Hirayama A, Nagase S, Takemura K, Koyama A, Ohba S, Narita M. Role of nitric oxide in the synthesis of guanidinosuccinic acid, an activator of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor. Kidney Int Suppl. 2001;78:S93–6. - PubMed
-
- Arias A, Garcia-Villoria J, Ribes A. Guanidinoacetate and creatine/creatinine levels in controls and patients with urea cycle defects. Mol Genet Metab. 2004;82(3):220–223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K01 RR000188/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM090310/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007526/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM90310/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK054450/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK081735/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RR00188/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- GM07526/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- RR19453/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U54 RR019453/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- K08 DK081735/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK54450/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000188/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD061221/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

