SPI-1-encoded type III secretion system of Salmonella enterica is required for the suppression of porcine alveolar macrophage cytokine expression
- PMID: 21314975
- PMCID: PMC3037896
- DOI: 10.1186/1297-9716-42-16
SPI-1-encoded type III secretion system of Salmonella enterica is required for the suppression of porcine alveolar macrophage cytokine expression
Abstract
Genes localized at Salmonella pathogenicity island-1 (SPI-1) are involved in Salmonella enterica invasion of host non-professional phagocytes. Interestingly, in macrophages, SPI-1-encoded proteins, in addition to invasion, induce cell death via activation of caspase-1 which also cleaves proIL-1β and proIL-18, precursors of 2 proinflammatory cytokines. In this study we were therefore interested in whether SPI-1-encoded type III secretion system (T3SS) may influence proinflammatory response of macrophages. To test this hypothesis, we infected primary porcine alveolar macrophages with wild-type S. Typhimurium and S. Enteritidis and their isogenic SPI-1 deletion mutants. ΔSPI1 mutants of both serovars invaded approx. 5 times less efficiently than the wild-type strains and despite this, macrophages responded to the infection with ΔSPI1 mutants by increased expression of proinflammatory cytokines IL-1β, IL-8, TNFα, IL-23α and GM-CSF. Identical macrophage responses to that induced by the ΔSPI1 mutants were also observed to the infection with sipB but not the sipA mutant. The hilA mutant exhibited an intermediate phenotype between the ΔSPI1 mutant and the wild-type S. Enteritidis. Our results showed that the SPI-1-encoded T3SS is required not only for cell invasion but in macrophages also for the suppression of early proinflammatory cytokine expression.
Figures
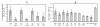


References
-
- Murray RA, Lee CA. Invasion genes are not required for Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium to breach the intestinal epithelium: evidence that salmonella pathogenicity island 1 has alternative functions during infection. Infect Immun. 2000;68:5050–5055. doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.9.5050-5055.2000. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Karasova D, Sebkova A, Havlickova H, Sisak F, Volf J, Faldyna M, Ondrackova P, Kummer V, Rychlik I. Influence of 5 major Salmonella pathogenicity islands on NK cell depletion in mice infected with Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis. BMC Microbiol. 2010;10:75. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-10-75. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rychlik I, Karasova D, Sebkova A, Volf J, Sisak F, Havlickova H, Kummer V, Imre A, Szmolka A, Nagy B. Virulence potential of five major pathogenicity islands (SPI-1 to SPI-5) of Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis for chickens. BMC Microbiol. 2009;9:268. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-9-268. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

