Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma with Epstein-Barr virus-positive Hodgkin-like cells
- PMID: 21315416
- PMCID: PMC3118938
- DOI: 10.1016/j.humpath.2010.10.014
Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma with Epstein-Barr virus-positive Hodgkin-like cells
Abstract
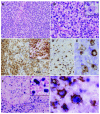
Hodgkin-like cells have been described in a variety of non-Hodgkin lymphomas including chronic lymphocytic leukemia and peripheral T-cell lymphoma. There have been rare reports in the Japanese population of human T-cell lymphotrophic virus-1-associated adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma harboring Hodgkin-like cells; however, no similar cases have been described in Western patients. We report a 53-year-old African American man who presented with progressive weakness and lethargy, and was found to have generalized lymphadenopathy and hypercalcemia. A lymph node biopsy showed involvement by adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma with scattered Epstein-Barr virus-positive cells, some of which resembled Hodgkin cells that had a B-cell phenotype, consistent with an Epstein-Barr virus-lymphoproliferative disorder. The patient had stage 4 disease with bone marrow involvement. In light of the associated B-cell lymphoproliferative process, the patient was treated with 6 cycles of intensive chemotherapy that targeted both the adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma and the Epstein-Barr virus-lymphoproliferative disorder that resulted in a complete response. An awareness of the association of Epstein-Barr virus-lymphoproliferative disorder with Hodgkin-like cells in the context of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma is necessary to avoid potential misdiagnosis and to aid in therapeutic decisions.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- White JD, Zaknoen SL, Kasten-Sportès C, Top LE, Navarro-Roman L, Nelson DL, et al. Infectious complications and immunodeficiency in patients with human T-cell lymphotropic virus I-associated adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Cancer. 1995;75:1598–1607. - PubMed
-
- Bishop JF, Schimpff SC, Diggs CH, Wiernik PH. Infections During Intensive Chemotherapy for Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma. Annals of Internal Medicine. 1981;95:549–555. - PubMed
-
- Ohshima K, Suzumiya J, Kato A, Tashiro K, Kikuchi M. Clonal HTLV-I-infected CD4+ T-lymphocytes and non-clonal non-HTLV-I- infected giant cells in incipient ATLL with Hodgkin-like histologic features. Int J Cancer. 1997;72:592–598. - PubMed
-
- Tanaka Y, Kondo T, Kishimoto W, Kanda J, Tashima M, Mizumoto C, et al. [Epstein-Barr virus-associated B cell lymphoproliferative disorder complicated in adult T-cell leukemia] Rinsho Ketsueki. 2008;49:263–269. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

