Lesions of the dorsomedial striatum disrupt prepulse inhibition
- PMID: 21315809
- PMCID: PMC3070827
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.01.041
Lesions of the dorsomedial striatum disrupt prepulse inhibition
Abstract
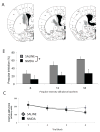
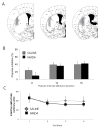
Prepulse inhibition (PPI) of startle is an experimentally tractable measure of sensorimotor gating that can be readily evaluated in mice, rats, monkeys, and humans. PPI is the inhibitory effect of a low-intensity stimulus, the prepulse, on the startle response to a subsequent high-intensity stimulus. PPI has garnered great interest as a marker of clinically relevant information processing abnormalities, because it is impaired in such neuropsychiatric conditions as schizophrenia, Tourette syndrome, and obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD). Pathology of the basal ganglia has been described in all three of these disorders, and it is therefore of great interest to determine the role of the basal ganglia in PPI. Previous work in rats described a PPI deficit after excitotoxic ventral striatal lesions and a more subtle attenuation after caudodorsal lesion, but no effect of other large lateral dorsal lesions. However, previous studies have not specifically investigated the role of the dorsomedial striatum in PPI. We investigated this issue using excitotoxic lesions in mice. We describe a marked reduction in PPI, at a variety of prepulse intensities, after bilateral lesions of dorsomedial striatum. There was no effect of lesion on baseline startle or habituation. In contrast, comparably sized lesions of the central dorsal striatum had no effect on PPI. These results reveal a role for the dorsomedial striatum in prepulse inhibition, which may have relevance for the abnormalities observed in this region in such disorders as Tourette syndrome and OCD.
Copyright © 2011 IBRO. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Arai S, Takuma K, Mizoguchi H, Ibi D, Nagai T, Takahashi K, Kamei H, Nabeshima T, Yamada K. Involvement of pallidotegmental neurons in methamphetamine- and MK-801-induced impairment of prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle reflex in mice: reversal by GABAB receptor agonist baclofen. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2008;33:3164–3175. - PubMed
-
- Braff DL, Geyer MA. Sensorimotor gating and schizophrenia. Human and animal model studies. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1990;47:181–188. - PubMed
-
- Braff DL, Geyer MA, Swerdlow NR. Human studies of prepulse inhibition of startle: normal subjects, patient groups, and pharmacological studies. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2001;156:234–258. - PubMed
-
- Brandt GN, Bonelli RM. Structural neuroimaging of the basal ganglia in schizophrenic patients: a review. Wien Med Wochenschr. 2008;158:84–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

