Red1 promotes the elimination of meiosis-specific mRNAs in vegetatively growing fission yeast
- PMID: 21317872
- PMCID: PMC3061036
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2011.32
Red1 promotes the elimination of meiosis-specific mRNAs in vegetatively growing fission yeast
Abstract
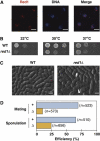
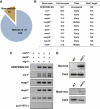
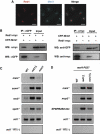
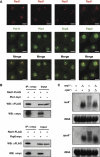
Meiosis-specific mRNAs are transcribed in vegetative fission yeast, and these meiotic mRNAs are selectively removed from mitotic cells to suppress meiosis. This RNA elimination system requires degradation signal sequences called determinant of selective removal (DSR), an RNA-binding protein Mmi1, polyadenylation factors, and the nuclear exosome. However, the detailed mechanism by which meiotic mRNAs are selectively degraded in mitosis but not meiosis is not understood fully. Here we report that Red1, a novel protein, is essential for elimination of meiotic mRNAs from mitotic cells. A red1 deletion results in the accumulation of a large number of meiotic mRNAs in mitotic cells. Red1 interacts with Mmi1, Pla1, the canonical poly(A) polymerase, and Rrp6, a subunit of the nuclear exosome, and promotes the destabilization of DSR-containing mRNAs. Moreover, Red1 forms nuclear bodies in mitotic cells, and these foci are disassembled during meiosis. These results demonstrate that Red1 is involved in DSR-directed RNA decay to prevent ectopic expression of meiotic mRNAs in vegetative cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A novel factor Iss10 regulates Mmi1-mediated selective elimination of meiotic transcripts.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Nov;41(21):9680-7. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt763. Epub 2013 Aug 26. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23980030 Free PMC article.
-
Rhn1, a nuclear protein, is required for suppression of meiotic mRNAs in mitotically dividing fission yeast.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e42962. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042962. Epub 2012 Aug 17. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22912768 Free PMC article.
-
Importance of polyadenylation in the selective elimination of meiotic mRNAs in growing S. pombe cells.EMBO J. 2010 Jul 7;29(13):2173-81. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2010.108. Epub 2010 May 28. EMBO J. 2010. PMID: 20512112 Free PMC article.
-
The selective elimination of messenger RNA underlies the mitosis-meiosis switch in fission yeast.Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2010;86(8):788-97. doi: 10.2183/pjab.86.788. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2010. PMID: 20948174 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms underlying the mitosis-meiosis decision.Chromosome Res. 2007;15(5):523-37. doi: 10.1007/s10577-007-1151-0. Chromosome Res. 2007. PMID: 17674143 Review.
Cited by
-
The fission yeast MTREC and EJC orthologs ensure the maturation of meiotic transcripts during meiosis.RNA. 2016 Sep;22(9):1349-59. doi: 10.1261/rna.055608.115. Epub 2016 Jun 30. RNA. 2016. PMID: 27365210 Free PMC article.
-
New romance between RNA degradation pathways: Mmi1 and RNAi meet on heterochromatic islands.EMBO J. 2012 May 16;31(10):2242-3. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.138. Epub 2012 May 1. EMBO J. 2012. PMID: 22549465 Free PMC article.
-
ZFC3H1 prevents RNA trafficking into nuclear speckles through condensation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Oct 11;49(18):10630-10643. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab774. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 34530450 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitination-dependent control of sexual differentiation in fission yeast.Elife. 2017 Aug 25;6:e28046. doi: 10.7554/eLife.28046. Elife. 2017. PMID: 28841135 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Ccr4-Not complex in heterochromatin formation at meiotic genes and subtelomeres in fission yeast.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2015 Aug 15;8:28. doi: 10.1186/s13072-015-0018-4. eCollection 2015. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2015. PMID: 26279681 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson P, Kedersha N (2009) RNA granules: post-transcriptional and epigenetic modulators of gene expression. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10: 430–436 - PubMed
-
- Averbeck N, Sunder S, Sample N, Wise JA, Leatherwood J (2005) Negative control contributes to an extensive program of meiotic splicing in fission yeast. Mol Cell 18: 491–498 - PubMed
-
- Bahler J, Wu JQ, Longtine MS, Shah NG, McKenzie A III, Steever AB, Wach A, Philippsen P, Pringle JR (1998) Heterologous modules for efficient and versatile PCR-based gene targeting in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Yeast 14: 943–951 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

