Regulation of effector and memory T-cell functions by type I interferon
- PMID: 21320124
- PMCID: PMC3075500
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2011.03412.x
Regulation of effector and memory T-cell functions by type I interferon
Abstract
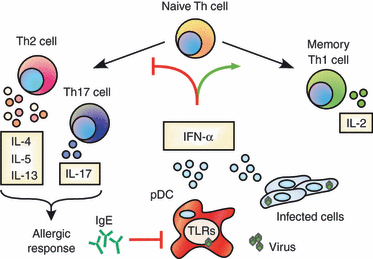
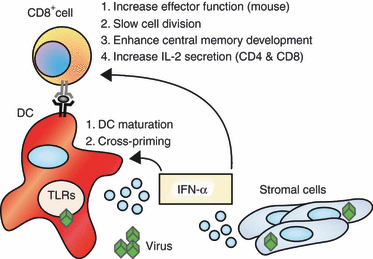
Type I interferon (IFN-α/β) is comprised of a family of highly related molecules that exert potent antiviral activity by interfering with virus replication and spread. IFN-α/β secretion is tightly regulated through pathogen sensing pathways that are operative in most somatic cells. However, specialized antigen-presenting plasmacytoid dendritic cells are uniquely equipped with the capacity to secrete extremely high levels of IFN-α/β, suggesting a key role for this cytokine in priming adaptive T-cell responses. Recent studies in both mice and humans have demonstrated a role for IFN-α/β in directly influencing the fate of both CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells during the initial phases of antigen recognition. As such, IFN-α/β, among other innate cytokines, is considered an important 'third signal' that shapes the effector and memory T-cell pool. Moreover, IFN-α/β also serves as a counter-regulator of T helper type 2 and type 17 responses, which may be important in the treatment of atopy and autoimmunity, and in the development of novel vaccine adjuvants.
© 2011 The Authors. Immunology © 2011 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Isaacs A, Lindenmann J, Valentine RC. Virus interference. II. Some properties of interferon. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1957;147:268–73. - PubMed
-
- Isaacs A, Lindenmann J. Virus interference. I. The interferon. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1957;147:258–67. - PubMed
-
- Stark GR, Kerr IM, Williams BR, Silverman RH, Schreiber RD. How cells respond to interferons. Annu Rev Biochem. 1998;67:227–64. - PubMed
-
- Hardy MP, Owczarek CM, Jermiin LS, Ejdeback M, Hertzog PJ. Characterization of the type I interferon locus and identification of novel genes. Genomics. 2004;84:331–45. - PubMed
-
- Pestka S, Krause CD, Walter MR. Interferons, interferon-like cytokines, and their receptors. Immunol Rev. 2004;202:8–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

