Sizing the lung of mechanically ventilated patients
- PMID: 21320330
- PMCID: PMC3221993
- DOI: 10.1186/cc10034
Sizing the lung of mechanically ventilated patients
Abstract
Introduction: This small observational study was motivated by our belief that scaling the tidal volume in mechanically ventilated patients to the size of the injured lung is safer and more 'physiologic' than scaling it to predicted body weight, i.e. its size before it was injured. We defined Total Lung Capacity (TLC) as the thoracic gas volume at an airway pressure of 40 cm H2O and tested if TLC could be inferred from the volume of gas that enters the lungs during a brief 'recruitment' maneuver.
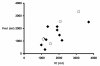
Methods: Lung volume at relaxed end expiration (Vrel) as well as inspiratory capacity (IC), defined as the volume of gas that enters the lung during a 5 second inflation to 40 cm H2O, were measured in 14 patients with respiratory failure. TLC was defined as the sum of IC and Vrel. The dependence of IC and Vrel on body mass index (BMI), respiratory system elastance and plateau airway pressure was assessed.
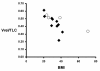
Results: TLC was reduced to 59 ± 23% of that predicted. Vrel/TLC, which averaged 0.45 ± 0.11, was no different than the 0.47 ± 0.04 predicted during health in the supine posture. The greater than expected variability in observed Vrel/TLC was largely accounted for by BMI. Vrel and IC were correlated (r = 0.76). Taking BMI into account strengthened the correlation (r = 0.92).
Conclusions: We conclude that body mass is a powerful determinant of lung volume and plateau airway pressure. Effective lung size can be easily estimated from a recruitment maneuver derived inspiratory capacity measurement and body mass index.
Figures

Comment in
-
When pressure does not mean volume? Body mass index may account for the dissociation.Crit Care. 2011;15(2):143. doi: 10.1186/cc10077. Epub 2011 Mar 25. Crit Care. 2011. PMID: 21457489 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Crapo RO, Morris AH, Clayton PD, Nixon CR. Lung volumes in healthy nonsmoking adults. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir. 1982;18:419–425. - PubMed
-
- Robinson JD, Lupkiewicz SM, Palenik L, Lopez LM, Ariet M. Determination of ideal body weight for drug dosage calculations. Am J Hosp Pharm. 1983;40:1016–1019. - PubMed
-
- Chiumello D, Carlesso E, Cadringher P, Caironi P, Valenza F, Polli F, Tallarini F, Cozzi P, Cressoni M, Colombo A, Marini JJ, Gattinoni L. Lung stress and strain during mechanical ventilation for acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008;178:346–355. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200710-1589OC. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

