Tropomyosin position on F-actin revealed by EM reconstruction and computational chemistry
- PMID: 21320445
- PMCID: PMC3037716
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2010.12.3697
Tropomyosin position on F-actin revealed by EM reconstruction and computational chemistry
Abstract
Electron microscopy and fiber diffraction studies of reconstituted F-actin-tropomyosin filaments reveal the azimuthal position of end-to-end linked tropomyosin molecules on the surface of actin. However, the longitudinal z-position of tropomyosin along F-actin is still uncertain. Without this information, atomic models of F-actin-tropomyosin filaments, free of constraints imposed by troponin or other actin-binding proteins, cannot be formulated, and thus optimal interfacial contacts between actin and tropomyosin remain unknown. Here, a computational search assessing electrostatic interactions for multiple azimuthal locations, z-positions, and pseudo-rotations of tropomyosin on F-actin was performed. The information gleaned was used to localize tropomyosin on F-actin, yielding an atomic model characterized by protein-protein contacts that primarily involve clusters of basic amino acids on actin subdomains 1 and 3 juxtaposed against acidic residues on the successive quasi-repeating units of tropomyosin. A virtually identical model generated by docking F-actin and tropomyosin atomic structures into electron microscopy reconstructions of F-actin-tropomyosin validated the above solution. Here, the z-position of tropomyosin alongside F-actin was defined by matching the seven broad and narrow motifs that typify tropomyosin's twisting superhelical coiled-coil to the wide and tapering tropomyosin densities seen in surface views of F-actin-tropomyosin reconstructions. The functional implications of the F-actin-tropomyosin models determined in this work are discussed.
Copyright © 2011 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

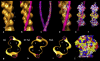
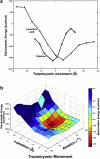
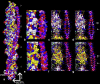
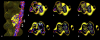
Comment in
-
Tropomyosin: the gatekeeper's view of the actin filament revealed.Biophys J. 2011 Feb 16;100(4):797-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2011.01.018. Biophys J. 2011. PMID: 21320421 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Perry S.V. What is the role of tropomyosin in the regulation of muscle contraction? J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 2003;24:593–596. - PubMed
-
- Brown J.H., Cohen C. Regulation of muscle contraction by tropomyosin and troponin: how structure illuminates function. Adv. Protein Chem. 2005;71:121–159. - PubMed
-
- Hitchcock-DeGregori S.E. Tropomyosin: function follows structure. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2008;644:60–72. - PubMed
-
- Gunning P.W., Schevzov G., Hardeman E.C. Tropomyosin isoforms: divining rods for actin cytoskeleton function. Trends Cell Biol. 2005;15:333–341. - PubMed
-
- Gunning P.W., O'Neill G., Hardeman E. Tropomyosin-based regulation of the actin cytoskeleton in time and space. Physiol. Rev. 2008;88:1–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

