Improving SNP discovery by base alignment quality
- PMID: 21320865
- PMCID: PMC3072548
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr076
Improving SNP discovery by base alignment quality
Abstract
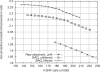
I propose a new application of profile Hidden Markov Models in the area of SNP discovery from resequencing data, to greatly reduce false SNP calls caused by misalignments around insertions and deletions (indels). The central concept is per-Base Alignment Quality, which accurately measures the probability of a read base being wrongly aligned. The effectiveness of BAQ has been positively confirmed on large datasets by the 1000 Genomes Project analysis subgroup.
Availability: http://samtools.sourceforge.net
Contact: hengli@broadinstitute.org.
Figures

References
-
- Durbin R., et al. Biological Sequence Analysis: Probabilistic Models of Proteins and Nucleic Acids. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press; 1998.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

