A diterpenoid derivative 15-oxospiramilactone inhibits Wnt/β-catenin signaling and colon cancer cell tumorigenesis
- PMID: 21321609
- PMCID: PMC3203668
- DOI: 10.1038/cr.2011.30
A diterpenoid derivative 15-oxospiramilactone inhibits Wnt/β-catenin signaling and colon cancer cell tumorigenesis
Abstract
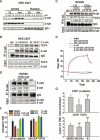
The Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway is a highly conserved pathway in organism evolution and regulates many biological processes. Aberrant activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway is closely related to tumorigenesis. In order to identify potent small molecules to treat the over-activated Wnt signaling-mediated cancer, such as colon cancer, we established a mammalian cell line-based reporter gene screening system. The screen revealed a diterpenoid derivative, 15-oxospiramilactone (NC043) that inhibits Wnt3a or LiCl-stimulated Top-flash reporter activity in HEK293T cells and growth of colon cancer cells, SW480 and Caco-2. Treatment of SW480 cells with NC043 led to decreases in the mRNA and/or protein expression of Wnt target genes Axin2, Cyclin D1 and Survivin , as well as decreases in the protein levels of Cdc25c and Cdc2. NC043 did not affect the cytosol-nuclear distribution and protein level of soluble β-catenin, but decreased β-catenin/TCF4 association in SW480 cells. Moreover, NC043 inhibited anchorage-independent growth and xenograft tumorigenesis of SW480 cells. Collectively these results demonstrate that NC043 is a novel small molecule that inhibits canonical Wnt signaling downstream of β-catenin stability and may be a potential compound for treating colorectal cancer.
Figures



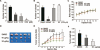
References
-
- Clevers H. Wnt/β-catenin signaling in development and disease. Cell. 2006;127:469–480. - PubMed
-
- Klaus A, Birchmeier W. Wnt signalling and its impact on development and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:387–398. - PubMed
-
- Bilic J, Huang YL, Davidson G, et al. Wnt induces LRP6 signalosomes and promotes dishevelled-dependent LRP6 phosphorylation. Science. 2007;316:1619–1622. - PubMed
-
- Mao J, Wang J, Liu B, et al. Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-5 binds to Axin and regulates the canonical Wnt signaling pathway. Mol Cell. 2001;7:801–809. - PubMed
-
- Giles RH, van Es JH, Clevers H. Caught up in a Wnt storm: Wnt signaling in cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003;1653:1–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

