Balloon catheter injury abolishes phenylephrine-induced relaxation in the rat contralateral carotid
- PMID: 21323906
- PMCID: PMC3111679
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01275.x
Balloon catheter injury abolishes phenylephrine-induced relaxation in the rat contralateral carotid
Abstract
Background and purpose: The consequences of compensatory responses to balloon catheter injury in rat carotid artery, on phenylephrine-induced relaxation and contraction in the contralateral carotid artery were studied.
Experimental approach: Relaxation and contraction concentration-response curves for phenylephrine were obtained for contralateral carotid arteries in the presence of indomethacin (COX inhibitor), SC560 (COX-1 inhibitor), SC236 (COX-2 inhibitor) or 4-hydroxytetramethyl-L-piperidine-1-oxyl (tempol; superoxide dismutase mimetic). Reactive oxygen species were measured in carotid artery endothelial cells fluorimetrically with dihydroethidium.
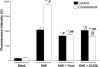
Key results: Phenylephrine-induced relaxation was abolished in contralateral carotid arteries from operated rats (E(max) = 0.01 ± 0.004 g) in relation to control (E(max) = 0.18 ± 0.005 g). Phenylephrine-induced contractions were increased in contralateral arteries (E(max) = 0.54 ± 0.009 g) in relation to control (E(max) = 0.38 ± 0.014 g). SC236 restored phenylephrine-induced relaxation (E(max) = 0.17 ± 0.004 g) and contraction (E(max) = 0.34 ± 0.018 g) in contralateral arteries. Tempol restored phenylephrine-induced relaxation (E(max) = 0.19 ± 0.012 g) and contraction (E(max) = 0.42 ± 0.014 g) in contralateral arteries, while apocynin did not alter either relaxation (E(max) = 0.01 ± 0.004 g) or contraction (E(max) = 0.54 ± 0.009 g). Dihydroethidium fluorescence was increased in contralateral samples (18 882 ± 435 U) in relation to control (10 455 ± 303 U). SC236 reduced the fluorescence in contralateral samples (8250 ± 365 U).
Conclusions and implications: Balloon catheter injury abolished phenylephrine-induced relaxation and increased phenylephrine-induced contraction in contralateral carotid arteries, through O(2) (-) derived from COX-2.
© 2011 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology © 2011 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures




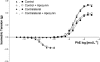
References
-
- Antonaccio MJ, Normandin D, Ferrer P. Reduced contractile function after balloon denudation of rat carotid arteries. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994;256:17–21. - PubMed
-
- Boer C, Scheffer GJ, de Lange JJ, Westerhof N, Sipkema P. Alpha1-adrenoceptor stimulation induces nitric oxide release in rat pulmonary arteries. J Vasc Res. 1999;36:79–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

