Cannabinoid receptor signalling in neurodegenerative diseases: a potential role for membrane fluidity disturbance
- PMID: 21323908
- PMCID: PMC3165948
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01277.x
Cannabinoid receptor signalling in neurodegenerative diseases: a potential role for membrane fluidity disturbance
Abstract
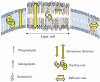
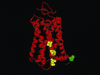
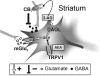
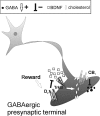
Type-1 cannabinoid receptor (CB(1)) is the most abundant G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) in the brain. CB(1) and its endogenous agonists, the so-called 'endocannabinoids (eCBs)', belong to an ancient neurosignalling system that plays important functions in neurodegenerative and neuroinflammatory disorders like Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and multiple sclerosis. For this reason, research on the therapeutic potential of drugs modulating the endogenous tone of eCBs is very intense. Several GPCRs reside within subdomains of the plasma membranes that contain high concentrations of cholesterol: the lipid rafts. Here, the hypothesis that changes in membrane fluidity alter function of the endocannabinoid system, as well as progression of particular neurodegenerative diseases, is described. To this end, the impact of membrane cholesterol on membrane properties and hence on neurodegenerative diseases, as well as on CB(1) signalling in vitro and on CB(1) -dependent neurotransmission within the striatum, is discussed. Overall, present evidence points to the membrane environment as a critical regulator of signal transduction triggered by CB(1) , and calls for further studies aimed at better clarifying the contribution of membrane lipids to eCBs signalling. The results of these investigations might be exploited also for the development of novel therapeutics able to combat disorders associated with abnormal activity of CB(1).
© 2011 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology © 2011 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cannabinoid receptors and endocannabinoids: role in neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative disorders.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2010 Nov;9(5):564-73. doi: 10.2174/187152710793361568. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2010. PMID: 20632970 Review.
-
Characterization of the endocannabinoid system, CB(1) receptor signalling and desensitization in human myometrium.Br J Pharmacol. 2011 Nov;164(5):1479-94. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01425.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21486283 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of control of neuron survival by the endocannabinoid system.Curr Pharm Des. 2008;14(23):2279-88. doi: 10.2174/138161208785740117. Curr Pharm Des. 2008. PMID: 18781978 Review.
-
The endocannabinoid system in gp120-mediated insults and HIV-associated dementia.Exp Neurol. 2010 Jul;224(1):74-84. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2010.03.025. Epub 2010 Mar 29. Exp Neurol. 2010. PMID: 20353779 Review.
-
Targeting the endocannabinoid system with cannabinoid receptor agonists: pharmacological strategies and therapeutic possibilities.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2012 Dec 5;367(1607):3353-63. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2011.0381. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2012. PMID: 23108552 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cannabinoid receptors distribution in mouse cortical plasma membrane compartments.Mol Brain. 2021 Jun 7;14(1):89. doi: 10.1186/s13041-021-00801-x. Mol Brain. 2021. PMID: 34099009 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-1β causes anxiety by interacting with the endocannabinoid system.J Neurosci. 2012 Oct 3;32(40):13896-905. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1515-12.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 23035099 Free PMC article.
-
Cannabinoid receptor type-1: breaking the dogmas.F1000Res. 2016 May 24;5:F1000 Faculty Rev-990. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.8245.1. eCollection 2016. F1000Res. 2016. PMID: 27239293 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endocannabinoids, related compounds and their metabolic routes.Molecules. 2014 Oct 24;19(11):17078-106. doi: 10.3390/molecules191117078. Molecules. 2014. PMID: 25347455 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid rafts in neurodegeneration and neuroprotection.Mol Neurobiol. 2014 Aug;50(1):130-48. doi: 10.1007/s12035-013-8614-4. Epub 2013 Dec 22. Mol Neurobiol. 2014. PMID: 24362851 Review.
References
-
- Alexander SPH, Mathie A, Peters JA. Guide to receptors and channels (GRAC) Br J Pharmacol. (>4th edn.) 2009;158:S1–S254. - PubMed
-
- Anderson RG, Kamen BA, Rothberg KG, Lacey SW. Potocytosis: sequestration and transport of small molecules by caveolae. Science. 1992;255:410–411. - PubMed
-
- Bari M, Paradisi A, Pasquariello N, Maccarrone M. Cholesterol-dependent modulation of type 1 cannabinoid receptors in nerve cells. J Neurosci Res. 2005a;81:275–283. - PubMed
-
- Bari M, Battista N, Fezza F, Finazzi-Agrò A, Maccarrone M. Lipid rafts control signaling of type-1 cannabinoid receptors in neuronal cells. Implications for anandamide-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 2005b;280:12212–12220. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

