Prospective evaluation of insulin resistance among endometrial cancer patients
- PMID: 21324431
- PMCID: PMC4286377
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajog.2010.11.033
Prospective evaluation of insulin resistance among endometrial cancer patients
Abstract
Objective: Obesity and estrogen are strong risk factors for endometrial cancer (EC). Whereas diabetes also increases the risk, little is known about related insulin resistance (IR). The purpose of this study was to determine the prevalence of IR in newly diagnosed EC patients.
Study design: EC patients from a large, metropolitan county were prospectively enrolled from 2005 to 2008. Fasting serum was analyzed for glucose and insulin. IR was defined as a history of diabetes or a quantitative insulin sensitivity check index (QUICKI) (1/[log fasting insulin + log fasting glucose]) value of less than 0.357.
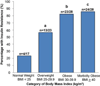
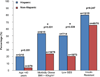
Results: Among 99 patients, diabetes was present in 30, and an abnormal QUICKI was found in 36 additional patients. Increased risk of IR was significantly associated with higher body mass index (P < .001), lower socioeconomic status (P = .007), and nulliparity (P = .029).
Conclusion: IR was highly prevalent in endometrial cancer patients, including nonobese women. Better characterization of metabolic risks in addition to obesity may provide avenues for targeted cancer prevention in the future.
Copyright © 2011 Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010 Epub. - PubMed
-
- Brinton LA, Berman ML, Mortel R, et al. Reproductive, menstrual, and medical risk factors for endometrial cancer: results from a case-control study. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1992;167:1317–1325. - PubMed
-
- Elwood JM, Cole P, Rothman KJ, Kaplan SD. Epidemiology of endometrial cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1977;59:1055–1060. - PubMed
-
- Goodman MT, Hankin JH, Wilkens LR, et al. Diet, body size, physical activity, and the risk of endometrial cancer. Cancer Res. 1997;57:5077–5085. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

