Kindlin-2 regulates podocyte adhesion and fibronectin matrix deposition through interactions with phosphoinositides and integrins
- PMID: 21325030
- PMCID: PMC3048888
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.076976
Kindlin-2 regulates podocyte adhesion and fibronectin matrix deposition through interactions with phosphoinositides and integrins
Abstract
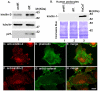
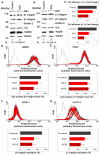
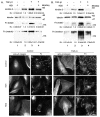
Kindlin-2 is a FERM and PH domain-containing integrin-binding protein that is emerging as an important regulator of integrin activation. How kindlin-2 functions in integrin activation, however, is not known. We report here that kindlin-2 interacts with multiple phosphoinositides, preferentially with phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate. Although integrin-binding is essential for focal adhesion localization of kindlin-2, phosphoinositide-binding is not required for this process. Using biologically and clinically relevant glomerular podocytes as a model system, we show that integrin activation and dependent processes are tightly regulated by kindlin-2: depletion of kindlin-2 reduced integrin activation, matrix adhesion and fibronectin matrix deposition, whereas overexpression of kindlin-2 promoted these processes. Furthermore, we provide evidence showing that kindlin-2 is involved in phosphoinositide-3-kinase-mediated regulation of podocyte-matrix adhesion and fibronectin matrix deposition. Mechanistically, kindlin-2 promotes integrin activation and integrin-dependent processes through interacting with both integrins and phosphoinositides. TGF-β1, a mediator of progressive glomerular failure, markedly increased the level of kindlin-2 and fibronectin matrix deposition, and the latter process was reversed by depletion of kindlin-2. Our results reveal important functions of kindlin-2 in the regulation of podocyte-matrix adhesion and matrix deposition and shed new light on the mechanism whereby kindlin-2 functions in these processes.
Figures





References
-
- Barisoni L., Mundel P. (2003). Podocyte biology and the emerging understanding of podocyte diseases. Am. J. Nephrol. 23, 353-360 - PubMed
-
- Byzova T. V., Goldman C. K., Pampori N., Thomas K. A., Bett A., Shattil S. J., Plow E. F. (2000). A mechanism for modulation of cellular responses to VEGF: activation of the integrins. Mol. Cell 6, 851-860 - PubMed
-
- Calderwood D. A. (2004). Integrin activation. J. Cell Sci. 117, 657-666 - PubMed
-
- Chivian D., Kim D. E., Malmstrom L., Schonbrun J., Rohl C. A., Baker D. (2005). Prediction of CASP6 structures using automated Robetta protocols. Proteins 61 Suppl. 7, 157-166 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

