BLM-DNA2-RPA-MRN and EXO1-BLM-RPA-MRN constitute two DNA end resection machineries for human DNA break repair
- PMID: 21325134
- PMCID: PMC3042158
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.2003811
BLM-DNA2-RPA-MRN and EXO1-BLM-RPA-MRN constitute two DNA end resection machineries for human DNA break repair
Abstract
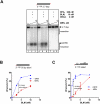
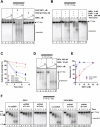
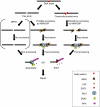
Repair of dsDNA breaks requires processing to produce 3'-terminated ssDNA. We biochemically reconstituted DNA end resection using purified human proteins: Bloom helicase (BLM); DNA2 helicase/nuclease; Exonuclease 1 (EXO1); the complex comprising MRE11, RAD50, and NBS1 (MRN); and Replication protein A (RPA). Resection occurs via two routes. In one, BLM and DNA2 physically and specifically interact to resect DNA in a process that is ATP-dependent and requires BLM helicase and DNA2 nuclease functions. RPA is essential for both DNA unwinding by BLM and enforcing 5' → 3' resection polarity by DNA2. MRN accelerates processing by recruiting BLM to the end. In the other, EXO1 resects the DNA and is stimulated by BLM, MRN, and RPA. BLM increases the affinity of EXO1 for ends, and MRN recruits and enhances the processivity of EXO1. Our results establish two of the core machineries that initiate recombinational DNA repair in human cells.
Figures



References
-
- Bae SH, Bae KH, Kim JA, Seo YS 2001. RPA governs endonuclease switching during processing of Okazaki fragments in eukaryotes. Nature 412: 456–461 - PubMed
-
- Brosh RM Jr, Li JL, Kenny MK, Karow JK, Cooper MP, Kureekattil RP, Hickson ID, Bohr VA 2000. Replication protein A physically interacts with the Bloom's syndrome protein and stimulates its helicase activity. J Biol Chem 275: 23500–23508 - PubMed
-
- Budd ME, Choe W, Campbell JL 2000. The nuclease activity of the yeast DNA2 protein, which is related to the RecB-like nucleases, is essential in vivo. J Biol Chem 275: 16518–16529 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
