Inhibition of the plasma membrane Ca2+ pump by CD44 receptor activation of tyrosine kinases increases the action potential afterhyperpolarization in sensory neurons
- PMID: 21325503
- PMCID: PMC3565434
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5764-10.2011
Inhibition of the plasma membrane Ca2+ pump by CD44 receptor activation of tyrosine kinases increases the action potential afterhyperpolarization in sensory neurons
Abstract
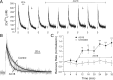
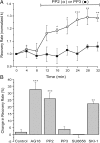
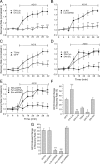
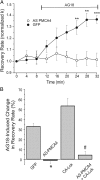
The cytoplasmic Ca(2+) clearance rate affects neuronal excitability, plasticity, and synaptic transmission. Here, we examined the modulation of the plasma membrane Ca(2+) ATPase (PMCA) by tyrosine kinases. In rat sensory neurons grown in culture, the PMCA was under tonic inhibition by a member of the Src family of tyrosine kinases (SFKs). Ca(2+) clearance accelerated in the presence of selective tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Tonic inhibition of the PMCA was attenuated in cells expressing a dominant-negative construct or shRNA directed to message for the SFKs Lck or Fyn, but not Src. SFKs did not appear to phosphorylate the PMCA directly but instead activated focal adhesion kinase (FAK). Expression of constitutively active FAK enhanced and dominant-negative or shRNA knockdown of FAK attenuated tonic inhibition. Antisense knockdown of PMCA isoform 4 removed tonic inhibition of Ca(2+) clearance, indicating that FAK acts on PMCA4. The hyaluronan receptor CD44 activates SFK-FAK signaling cascades and is expressed in sensory neurons. Treating neurons with a CD44-blocking antibody or short hyaluronan oligosaccharides, which are produced during injury and displace macromolecular hyaluronan from CD44, attenuated tonic PMCA inhibition. Ca(2+)-activated K(+) channels mediate a slow afterhyperpolarization in sensory neurons that was inhibited by tyrosine kinase inhibitors and enhanced by knockdown of PMCA4. Thus, we describe a novel kinase cascade in sensory neurons that enables the extracellular matrix to alter Ca(2+) signals by modulating PMCA-mediated Ca(2+) clearance. This signaling pathway may influence the excitability of sensory neurons following injury.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Interleukin-1β activates an Src family kinase to stimulate the plasma membrane Ca2+ pump in hippocampal neurons.J Neurophysiol. 2016 Apr;115(4):1875-85. doi: 10.1152/jn.00541.2015. Epub 2016 Feb 3. J Neurophysiol. 2016. PMID: 26843596 Free PMC article.
-
Bradykinin and ATP accelerate Ca(2+) efflux from rat sensory neurons via protein kinase C and the plasma membrane Ca(2+) pump isoform 4.Neuron. 2002 Jan 3;33(1):113-22. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(01)00557-8. Neuron. 2002. PMID: 11779484
-
Ca2+-dependent, stimulus-specific modulation of the plasma membrane Ca2+ pump in hippocampal neurons.J Neurophysiol. 2009 May;101(5):2563-71. doi: 10.1152/jn.90774.2008. Epub 2009 Feb 25. J Neurophysiol. 2009. PMID: 19244356 Free PMC article.
-
The regulatory function of plasma-membrane Ca(2+)-ATPase (PMCA) in the heart.Biochem Soc Trans. 2007 Nov;35(Pt 5):927-30. doi: 10.1042/BST0350927. Biochem Soc Trans. 2007. PMID: 17956248 Review.
-
Evaluation of plasma membrane calcium/calmodulin-dependent ATPase isoform 4 as a potential target for fertility control.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2010;(198):79-95. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-02062-9_6. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20839088 Review.
Cited by
-
Extracellular matrix hyaluronan signals via its CD44 receptor in the increased responsiveness to mechanical stimulation.Neuroscience. 2016 Jun 2;324:390-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.03.032. Epub 2016 Mar 18. Neuroscience. 2016. PMID: 26996509 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-1β activates an Src family kinase to stimulate the plasma membrane Ca2+ pump in hippocampal neurons.J Neurophysiol. 2016 Apr;115(4):1875-85. doi: 10.1152/jn.00541.2015. Epub 2016 Feb 3. J Neurophysiol. 2016. PMID: 26843596 Free PMC article.
-
CD44 Signaling Mediates High Molecular Weight Hyaluronan-Induced Antihyperalgesia.J Neurosci. 2018 Jan 10;38(2):308-321. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2695-17.2017. Epub 2017 Nov 24. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29175954 Free PMC article.
-
Decreases in plasma membrane Ca²⁺-ATPase in brain synaptic membrane rafts from aged rats.J Neurochem. 2012 Dec;123(5):689-99. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2012.07918.x. Epub 2012 Oct 11. J Neurochem. 2012. PMID: 22889001 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms Mediating High-Molecular-Weight Hyaluronan-Induced Antihyperalgesia.J Neurosci. 2020 Aug 19;40(34):6477-6488. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0166-20.2020. Epub 2020 Jul 14. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32665406 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bozulic LD, Malik MT, Dean WL. Effects of plasma membrane Ca(2+) -ATPase tyrosine phosphorylation on human platelet function. J Thromb Haemost. 2007;5:1041–1046. - PubMed
-
- Burette A, Rockwood JM, Strehler EE, Weinberg RJ. Isoform-specific distribution of the plasma membrane Ca2+ ATPase in the rat brain. J Comp Neurol. 2003;467:464–476. - PubMed
-
- Cabodi S, Di Stefano P, Leal Mdel P, Tinnirello A, Bisaro B, Morello V, Damiano L, Aramu S, Repetto D, Tornillo G, Defilippi P. Integrins and signal transduction. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010;674:43–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
