The relationship between duration of initial alcohol exposure and persistence of molecular tolerance is markedly nonlinear
- PMID: 21325511
- PMCID: PMC3758537
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5429-10.2011
The relationship between duration of initial alcohol exposure and persistence of molecular tolerance is markedly nonlinear
Abstract
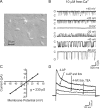
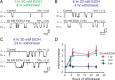
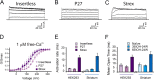
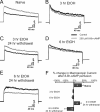
The neuronal calcium- and voltage-activated BK potassium channel is modulated by ethanol, and plays a role in behavioral tolerance in vertebrates and invertebrates. We examine the influence of temporal parameters of alcohol exposure on the characteristics of BK molecular tolerance in the ventral striatum, an important component of brain reward circuitry. BK channels in striatal neurons of C57BL/6J mice exhibited molecular tolerance whose duration was a function of exposure time. After 6 h exposure to 20 mm (0.09 mg%) ethanol, alcohol sensitivity was suppressed beyond 24 h after withdrawal, while after a 1 or 3 h exposure, sensitivity had significantly recovered after 4 h. This temporally controlled transition to persistent molecular tolerance parallels changes in BK channel isoform profile. After withdrawal from 6 h, but not 3 h alcohol exposure, mRNA levels of the alcohol-insensitive STREX (stress axis-regulated exon) splice variant were increased. Moreover, the biophysical properties of BK channels during withdrawal from 6 h exposure were altered, and match the properties of STREX channels exogenously expressed in HEK 293 cells. Our results suggest a temporally triggered shift in BK isoform identity. Once activated, the transition does not require the continued presence of alcohol. We next determined whether the results obtained using cultured striatal neurons could be observed in acutely dissociated striatal neurons, after alcohol administration in the living mouse. The results were in remarkable agreement with the striatal culture data, showing persistent molecular tolerance after injections producing 6 h of intoxication, but not after injections producing only 3 h of intoxication.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Regulation of STREX exon large conductance, calcium-activated potassium channels by the beta4 accessory subunit.Neuroscience. 2007 Nov 23;149(4):789-803. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.07.066. Epub 2007 Sep 12. Neuroscience. 2007. PMID: 17945424 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of BK Channels by Ethanol.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2016;128:239-79. doi: 10.1016/bs.irn.2016.03.019. Epub 2016 May 12. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 27238266 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Posttranscriptional regulation of BK channel splice variant stability by miR-9 underlies neuroadaptation to alcohol.Neuron. 2008 Jul 31;59(2):274-87. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.05.032. Neuron. 2008. PMID: 18667155 Free PMC article.
-
Time-Dependent Effects of Ethanol on BK Channel Expression and Trafficking in Hippocampal Neurons.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2015 Sep;39(9):1619-31. doi: 10.1111/acer.12808. Epub 2015 Aug 6. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2015. PMID: 26247146 Free PMC article.
-
BK channel and alcohol, a complicated affair.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2010;91:321-38. doi: 10.1016/S0074-7742(10)91010-6. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2010. PMID: 20813247 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative mRNA profile analysis from NAc of adolescent male mice after binge-like alcohol exposure eliciting deficits in context fear extinction learning.PLoS One. 2025 Jun 25;20(6):e0322576. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0322576. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40560842 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing ethanol's actions in the suprachiasmatic circadian clock using in vivo and in vitro approaches.Alcohol. 2015 Jun;49(4):321-339. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2014.07.016. Epub 2014 Oct 18. Alcohol. 2015. PMID: 25457753 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ethanol modulation of mammalian BK channels in excitable tissues: molecular targets and their possible contribution to alcohol-induced altered behavior.Front Physiol. 2014 Dec 2;5:466. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2014.00466. eCollection 2014. Front Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25538625 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of alcohol on the membrane excitability and synaptic transmission of medium spiny neurons in the nucleus accumbens.Alcohol. 2012 Jun;46(4):317-27. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2011.12.002. Epub 2012 Mar 24. Alcohol. 2012. PMID: 22445807 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BK ZERO isoform HEK293 stably transfected cell lines differing 3'UTRs to assess miR-9 regulation.PLoS One. 2024 Mar 19;19(3):e0298966. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0298966. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38502673 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmed SH, Koob GF. Transition from moderate to excessive drug intake: change in hedonic set point. Science. 1998;282:298–300. - PubMed
-
- Behrens R, Nolting A, Reimann F, Schwarz M, Waldschütz R, Pongs O. hKCNMB3 and hKCNMB4, cloning and characterization of two members of the large-conductance calcium-activated potassium channel beta subunit family. FEBS Lett. 2000;474:99–106. - PubMed
-
- Borlikova GG, Le Merrer J, Stephens DN. Previous experience of ethanol withdrawal increases withdrawal-induced c-fos expression in limbic areas, but not withdrawal-induced anxiety and prevents withdrawal-induced elevations in plasma corticosterone. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2006;185:188–200. - PubMed
-
- Brewer GJ, Torricelli JR, Evege EK, Price PJ. Optimized survival of hippocampal neurons in B27-supplemented Neurobasal, a new serum-free medium combination. J Neurosci Res. 1993;35:567–576. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
