WRP/srGAP3 facilitates the initiation of spine development by an inverse F-BAR domain, and its loss impairs long-term memory
- PMID: 21325512
- PMCID: PMC3541779
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4433-10.2011
WRP/srGAP3 facilitates the initiation of spine development by an inverse F-BAR domain, and its loss impairs long-term memory
Abstract
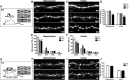
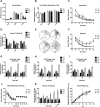
The WAVE-associated Rac GAP, WRP, is thought to regulate key aspects of synapse development and function and may be linked to mental retardation in humans. WRP contains a newly described inverse F-BAR (IF-BAR) domain of unknown function. Our studies show that this domain senses/facilitates outward protrusions analogous to filopodia and that the molecular basis for this is likely explained by a convex lipid-binding surface on the WRP IF-BAR domain. In dendrites the IF-BAR domain of WRP forms a bud on the shaft from which precursors to spines emerge. Loss of WRP in vivo and in vitro results in reduced density of spines. In vivo this is primarily a loss of mushroom-shaped spines. Developmentally, WRP function is critical at the onset of spinogenesis, when dendritic filopodia are prevalent. Finally, because WRP is implicated in mental retardation, behaviors of WRP heterozygous and null mice have been evaluated. Results from these studies confirm that loss of WRP is linked to impaired learning and memory.
Figures
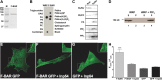

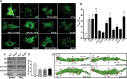
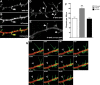
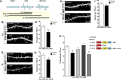
References
-
- Aspenström P. Roles of F-BAR/PCH proteins in the regulation of membrane dynamics and actin reorganization. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2009;272:1–31. - PubMed
-
- Banker G, Goslin K. Developments in neuronal cell culture. Nature. 1988;336:185–186. - PubMed
-
- Carlisle HJ, Kennedy MB. Spine architecture and synaptic plasticity. Trends Neurosci. 2005;28:182–187. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
