Genome-wide association study identifies genetic variants influencing F-cell levels in sickle-cell patients
- PMID: 21326311
- PMCID: PMC5825003
- DOI: 10.1038/jhg.2011.12
Genome-wide association study identifies genetic variants influencing F-cell levels in sickle-cell patients
Abstract
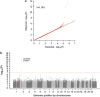
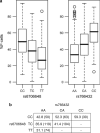
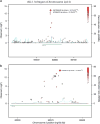
Fetal hemoglobin (HbF) level has emerged as an important prognostic factor in sickle-cell disease (SCD) and can be measured by the proportion of HbF-containing erythrocytes (F-cells). Recently, BCL11A (zinc-finger protein) was identified as a regulator of HbF, and the strongest association signals were observed either directly for rs766432 or for correlated single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). To identify additional independently associated genetic variants, we performed a genome-wide association study (GWAS) on the proportion of F-cells in individuals of African ancestry with SCD from the Silent Infarct Transfusion (SIT) Trial cohort. Our study not only confirms the association of rs766432 (P-value <3.32 × 10(-13)), but also identifies an independent novel intronic SNP, rs7606173, associated with F-cells (P-value <1.81 × 10(-15)). The F-cell variances explained independently by these two SNPs are ∼13% (rs7606173) and ∼11% (rs766432), whereas, together they explain ∼16%. Additionally, in men, we identify a novel locus on chromosome 17, glucagon-like peptide-2 receptor (GLP2R), associated with F-cell regulation (rs12103880; P-value <3.41 × 10(-8)). GLP2R encodes a G protein-coupled receptor and involved in proliferative and anti-apoptotic cellular responses. These findings highlight the importance of denser genetic screens and suggest further exploration of the BCL11A and GLP2R loci to gain additional insight into HbF/F-cell regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Motulsky AG. Frequency of sickling disorders in U.S. blacks. N. Engl. J. Med. 1973;288:31–33. - PubMed
-
- Platt OS, Brambilla DJ, Rosse WF, Milner PF, Castro O, Steinberg MH, et al. Mortality in sickle cell disease. Life expectancy and risk factors for early death. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994;330:1639–1644. - PubMed
-
- Watson J. The significance of the paucity of sickle cells in newborn Negro infants. Am. J. Med. Sci. 1948;215:419–423. - PubMed
-
- Jacob GF, Raper AB. Hereditary persistence of foetal haemoglobin production, and its interaction with the sickle-cell trait. Br. J. Haematol. 1958;4:138–149. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
