Vascular complications associated with percutaneous biliary drainage: a report of three cases
- PMID: 21326476
- PMCID: PMC3036326
- DOI: 10.1055/s-2007-985742
Vascular complications associated with percutaneous biliary drainage: a report of three cases
Abstract
Percutaneous biliary drainage is a common interventional radiology procedure. It is usually performed in the setting of biliary obstruction, benign or malignant, after endoscopic approach failed or is technically not possible. Percutaneous biliary drainage has a relatively low complication rate, and most complications that occur are usually self-limited. Major complications, however, can occur. In this article, we report three major hemorrhagic complications and their management. They include hemorrhage secondary to fistula formation and pseudoaneurysm formation occurring several days to weeks subsequent to the initial drain placement.
Keywords: Pseudoaneurysm; complication; fistula; percutaneous biliary drainage.
Figures
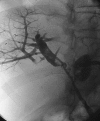
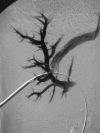

References
-
- Ferrucci J T, Jr, Meuller P R, Harbin W P. Percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage: technique, results, and applications. Radiology. 1980;135:1–13. - PubMed
-
- Mueller P R, vanSonnenberg E, Ferrucci J T., Jr Percutaneous biliary drainage: technical and catheter-related problems in 200 procedures. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1982;138:17–23. - PubMed
-
- Burke D R, Lewis C A, Cardella J F, et al. Quality improvement guidelines for percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography and biliary drainage. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2003;14:S243–S246. - PubMed
-
- Born P, Rosch T, Triptrap A, et al. Long-term results of percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage for benign and malignant bile duct strictures. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1998;33:544–549. - PubMed
-
- Hamlin J A, Friedman M, Stein M G, Bray J F. Percutaneous biliary drainage: complications of 118 consecutive catheterizations. Radiology. 1986;158:199–203. - PubMed

