Antidepressants for agitation and psychosis in dementia
- PMID: 21328305
- PMCID: PMC12214452
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD008191.pub2
Antidepressants for agitation and psychosis in dementia
Abstract
Background: Agitation and psychosis are common among older adults with dementia and are challenging to manage. At the present time, little is known about the efficacy and safety of antidepressant medications when used to treat these symptoms.
Objectives: To assess the safety and efficacy of antidepressants in treating psychosis and agitation in older adults with Alzheimer's disease, vascular, or mixed dementia.
Search strategy: We searched the Cochrane Dementia and Cognitive Improvement Group's Specialized Register which included Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (The Cochrane Library 2009, Issue 3), MEDLINE (January 1950 to October 2009), EMBASE (1980 - October 2009), CINAHL (all dates - October 2009) and PsycINFO (1806 to October 2009).
Selection criteria: Randomized, controlled trials of antidepressants (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), tricyclic antidepressants, trazodone, and other antidepressants), compared to either placebo or comparator medications (typical or atypical antipsychotics, anticonvulsants, benzodiazepines, cholinesterase inhibitors, memantine or other medications) for treatment of agitation or psychosis in older adults with dementia.
Data collection and analysis: Two authors independently assessed trial quality and extracted trial data. We collected information on efficacy as measured by dementia neuropsychiatric symptom rating scales and adverse effects. Study authors were contacted for additional information.
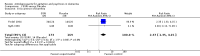
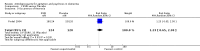
Main results: Nine trials including a total of 692 individuals were included in the review. Five studies compared SSRIs to placebo and two studies were combined in a meta-analysis for the outcome of change in Cohen-Mansfield Agitation Inventory (CMAI) scores. There was a significant difference between antidepressants and placebo on measures of agitation as reported on the change in CMAI total score (mean difference (MD), -0.89, 95% CI, -1.22 to -0.57) although the results were heavily weighted by one large study. There were no significant differences in change in behavioral symptoms of dementia for SSRIs compared to placebo in the one study that reported on changes in the Neuropsychiatric Inventory and Behavioral Pathology in Dementia scales. One study comparing citalopram to placebo found a significant difference in NPS as measured on the Neurobehavioral Rating Scale (NBRS) after controlling for baseline severity NBRS score although the unadjusted mean difference was not statistically significant (MD - 7.70, 95% CI: -16.57 to 1.17). There was no difference in the rates of trial withdrawals due to adverse events for SSRIs compared to placebo for four studies reporting this outcome (relative risk (RR), 1.07, 95% CI: 0.55 to 2.11) or in the number of trial withdrawals due to any cause in the three studies reporting this outcome (RR, 0.91, 95% CI, 0.65 to 1.26). One study compared the SSRI citalopram to the atypical antipsychotic risperidone and found no difference in NBRS scores, trial withdrawals due to any cause or trial withdrawals due to adverse events although the rates of adverse events as measured on the UKU side effect scale total score were lower for citalopram (MD -2.82, 95% CI: -4.94 to -0.70). Three studies compared SSRIs to typical antipsychotics. In meta-analysis of two studies there was no statistically significant differences in changes in CMAI total scores (MD, 4.66, 95% CI: -3.58 to 12.90). There was also no difference in trial withdrawals due to any cause or due to adverse events for SSRIs compared to typical antipsychotics. One study of trazodone compared to placebo did not find any significant difference in change in CMAI total scores (MD, 5.18, 95% CI, -2.86 to 13.22) or trial withdrawals due to any cause (RR, 1.06, 95% CI, 0.54 to 2.09). Two studies comparing trazodone to haloperidol also failed to detect any difference in change in CMAI total scores (MD, 3.28, 95% CI, -3.28 to 9.85) or trial withdrawals due to any cause (RR, 0.79, 95% CI, 0.43 to 1.46).
Authors' conclusions: Currently there are relatively few studies of antidepressants for the treatment of agitation and psychosis in dementia. The SSRIs sertraline and citalopram were associated with a reduction in symptoms of agitation when compared to placebo in two studies. Both SSRIs and trazodone appear to be tolerated reasonably well when compared to placebo, typical antipsychotics and atypical antipsychotics. Future studies involving more subjects are required to determine if SSRIs, trazodone, or other antidepressants are safe and effective treatments for agitation and psychosis in dementia.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Herrmann has received research support and/or speaker's honouraria from Lundbeck, Janssen‐Ortho, Pfizer, Novartis, Wyeth, and Eli Lilly. The remaining authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

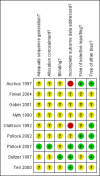



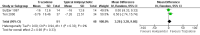











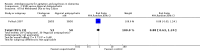




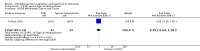








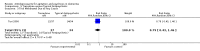




Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Auchus 1997 {published data only}
-
- Auchus AP, Bissey‐Black C. Pilot Study of Haloperidol, Fluoxetine, and Placebo for Agitation in Alzheimer's Disease. Journal of Neuropsychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences 1997;9(4):591‐593. - PubMed
Finkel 2004 {published data only}
-
- Clary C, McRae T, Griesing T, Whalen E. The safety of donepezil and sertraline for the management of behavioral symptoms in patients with Alzheimer's disease. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology. 2000:S267.
-
- Finkel S, McRae T, Burt T. Sertraline and Donepezil Demonstrate Similar Tolerability Compared to Donepezil Alone in Non‐Depressed Patients with Alzheimer's Disease. American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2001;9 (supplement 1):65.
-
- Finkel SI, Mintzer J, Burt T, McRae T. Sertraline augmentation reduces behavioral symptoms in outpatients with Alzheimer's disease treated with donepezil.. European Neuropsychopharmacology. 2002; Vol. 12 (supplement 3):S374.
-
- Finkel SI, Mintzer JE, Dysken M, Krishnan KRR, Burt T, McRae T. A randomized, placebo‐controlled study of the efficacy and safety of sertraline in the treatment of the behavioral manifestations of Alzheimer's disease in outpatients treated with donepezil. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2004;19(1):9‐18. - PubMed
-
- McRae, Griesing T, Whalen E. Donepezil and Sertraline for the Management of Behavioral Symptoms in Patients with Alzheimer's Disease. Neurology. 2000; Vol. 54 (supplement 3):A416.
Gaber 2001 {published data only}
-
- Gaber S, Ronzoni S, Bruno A, Biagi A. Sertraline versus small doses of haloperidol in the treatment of agitated behavior in patients with dementia. Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics 2001, (Supplement 7):159‐162. - PubMed
Nyth 1990 {published data only}
-
- Elgen K, Gottfries CG, Nyth AL. Effekt av citalopram pa emosjonelle forstyrrelser hos pasienter med Alzheimer demens. Nordic Journal of Psychiatry 1991;45(S23):23‐27.
-
- Nyth AL, Gottfries CG. The Clinical Efficacy of Emotional Disturbances in Dementia Disorders. Bristish Journal of Psychiatry 1990;157:894‐901. - PubMed
Olafsson 1992 {published data only}
-
- Olafsson K, Jorgensen S, Jensen HV, Bille A, Arup P, Andersen J. Fluvoxamine in the treatment of demented elderly patients: a double‐blind, placebo controlled study. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1992;85:453‐456. - PubMed
Pollock 2002 {published data only}
-
- Pollock B, Rosen J, Mulsant B, Sweet R, Marin R, Jacob N. Placebo‐controlled comparison of citalopram versus perphenazine for acute treatment of severe behavioral disturbances associated with dementia.. 14th Annual Meeting of the American Association for Geriatric Psychiatry. San Francisco, CA, 23rd ‐ 26th February.
-
- Pollock BG, Mulsant BH, Rosen J, Sweet RA, Mazumdar S, Barucha A, et al. Comparison of citalopram, perphenazine, and placebo for the acute treatment of psychosis and behavioral disturbances in hospitalized, demented patients. American Journal of Psychiatry 2002;159(3):460‐465. - PubMed
Pollock 2007 {published data only}
-
- Pollock BG, Mulsant BH, Rosen J, Mazumdar S, Blakesley RE, Houck PR, et al. A double‐blind comparison of citalopram and risperidone for the treatment of behavioral and psychotic symptoms associated with dementia. American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2007;15(11):942‐952. - PubMed
Sultzer 1997 {published data only}
-
- Sultzer DL, Gray KF, Gunay I, Berisford A, Mahler ME. A Double‐Blind Comparison of Trazodone and Haloperidol for Treatment of Agitation in Patients with Dementia. American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 1997;5(1):60‐69. - PubMed
-
- Sultzer DL, Gray KF, Gunay I, Wheatley MV, Mahler ME. Does Behavioral Improvement with Haloperidol or Trazodone Depend on Psychosis or Mood Symptoms in Patients with Dementia?. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2001;49(10):1294‐1300. - PubMed
Teri 2000 {published data only}
-
- Teri L, Peskind E, Raskind M, Weiner MF, Tractenberg RE, Foster NL, et al. Treatment of agitation in AD: A randomized, placebo‐controlled trial. Neurology 2000;55(9):1271‐1278. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Auer 1996 {published data only}
-
- Auer SR, Monteiro I, Torossian C, Sinaiko E, Boksay I, Reisberg B. The treatment of behavioral symptoms in dementia: haloperidol, thioridazine and fluoxetine: a double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, eight month study. Neurobiology of Aging 1996; Vol. 17, issue supplement 4:162. [CN‐00362268]
Baumann 2001 {published data only}
-
- Baumann P, Eap C B, Zullino D F. Fluvoxamine and perphenazine for psychosis in Alzheimer's disease: pharmacokinetic considerations. Journal of Nervous & Mental Disease 2001;189(11):798‐9. - PubMed
Bentham 1990 {published data only}
-
- Bentham P W. Preliminary communication. A double‐blind placebo‐controlled trial of L‐tryptophan to assess the degree of cognitive and behavioural improvement in patients with Alzheimer‐type dementia and to compare differential response in clinical sub‐groups. International Clinical Psychopharmacology 1990;5(4):261‐72. - PubMed
Burke 1997 {published data only}
-
- Burke WJ, Dewan V, Wengel SP, Roccaforte WH, Nadolny GC, Folks D. The Use of Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors for Depression and Psychosis Complicating Dementia. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 1997;12(5):519‐525. - PubMed
Burke 1997a {published data only}
-
- Burke W J, Dewan V, Wengel S P, Roccaforte W H, Nadolny G C, Folks D G. The use of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors for depression and psychosis complicating dementia.[see comment]. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 1997;12(5):519‐25. - PubMed
Cakir 2008 {published data only}
Dehlin 1985 {published data only}
-
- Dehlin O, Hedenrud B, Jansson P, Norgard J. A double‐blind comparison of alaproclate and placebo in the treatment of patients with senile dementia. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 1985;71(2):190‐196. - PubMed
Devanand 2003 {published data only}
-
- Devanand D P, Pelton G H, Marston K, Camacho Y, Roose S P, Stern Y, et al. Sertraline treatment of elderly patients with depression and cognitive impairment. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2003;18(2):123‐30. - PubMed
Geldmacher 1994 {published data only}
-
- Geldmacher D S, Waldman A J, Doty L, Heilman K M. Fluoxetine in dementia of the Alzheimer's type: prominent adverse effects and failure to improve cognition. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1994;55(4):161. - PubMed
Kim 2000 {published data only}
-
- Kim KY, Bader GM, Jones E. Citalopram for Verbal Agitation in Patients with Dementia. Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry Neurology 2000;13(2):53‐55. - PubMed
Lawlor 1991 {published data only}
-
- Lawlor B A, Sunderland T, Mellow A M, Molchan S E, Martinez R, Murphy D L. A pilot placebo‐controlled study of chronic m‐CPP administration in Alzheimer's disease. Biological Psychiatry 1991;30(2):140‐4. - PubMed
Lawlor 1994 {published data only}
-
- Lawlor BA, Radcliffe J, Molchan RA, Hill JL, Sunderland T. A pilot placebo‐controlled study of trazodone and buspirone in Alzheimer's disease. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 1994;9(1):55‐59.
Levkovitz 2001 {published data only}
-
- Levkovitz Y, Bloch Y, Kaplan D, Diskin A, Abramovitchi I. Fluvoxamine for Psychosis in Alzheimer's Disease. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 2001;189(2):126‐129. - PubMed
Lyketsos 2000 {published data only}
-
- Lyketsos C G, Sheppard J M, Steele C D, Kopunek S, Steinberg M, Baker A S, et al. Randomized, placebo‐controlled, double‐blind clinical trial of sertraline in the treatment of depression complicating Alzheimer's disease: initial results from the Depression in Alzheimer's Disease study. American Journal of Psychiatry 2000;157(10):1686‐9. - PubMed
-
- Steinberg M, Munro CA, Samus Q, Rabins PV, Brandt J, Lyketsos CG. Patient predictors of response to treatment of depression in Alzheimer's disease: the DIADS study. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2004;19(2):144‐150. - PubMed
Mervis 1991 {published data only}
-
- Mervis JR, Ganzell S, Fitten J, Daum G, Tripodis K, Takayesu S. Comparison of Carbamazepine and Trazodone in the Control of Aggression/Agitation in Demented Institutionalized Patients; A Randomized Double Blind Parallel Study. Journal of the American Geriatric Society 1991;39(8):A75.
Passeri 1987a {published data only}
-
- Passeri M, Cucinotta D, Mello M, Bizière K. Comparison of minaprine and placebo in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease and multi‐infarct dementia. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 1987;2(2):97‐103.
-
- Passeri M, Cucinotta D, Mello M, Storchi G, Roncucci R, Biziere K. Minaprine for senile dementia. Lancet 1985;1(8432):824. - PubMed
Passeri 1993 {published data only}
-
- Passeri M, Cucinotta D, Abate G, Senin U, Ventura A, Stramba Badiale M, et al. Oral 5'‐methyltetrahydrofolic acid in senile organic mental disorders with depression: results of a double‐blind multicenter study. Aging‐Clinical & Experimental Research 1993;5(1):63‐71. - PubMed
Ramadan 1999 {published data only}
-
- Ramadan F H, Naughton B J. Paroxetine for verbal agitation. Annals of Long‐Term Care 1999;7(7):282‐6.
Reifler 1989 {published data only}
-
- Reifler BV, Teri L, Raskind M, Veith R, Barnes R, White E, et al. Double‐Blind Trial of Imipramine in Alzheimer's Disease Patients With and Without Depression. American Journal of Psychiatry 1989;146(1):45‐49. - PubMed
Scharre 2003 {published data only}
-
- Scharre D W, Davis R A, Warner J L, Chang S I, Beversdorf D Q, Scharre Douglas W, et al. A pilot open‐label trial of citalopram for restless activity and aberrant motor behaviors in Alzheimer disease. American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2003;11(6):687‐91. - PubMed
Schneider 2009 {published data only}
-
- Schneider LS, Vigen CL, Mack WJ, Davis SM, Sultzer DL, Weintraub D, et al. Effectiveness of Citalopram Compared to Atypical Antipsychotics in Alzheimer's Disease Patients Who Discontinued Their Initially Assigned Treatment: CATIE‐AD Phase II Results. American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2009;17(3 (Supplement 1)):A77.
Siddique 2009 {published data only}
Timmons 2004 {published data only}
-
- Timmons S, O' Sullivan C, Barry P, O'Connor M, O' Mahony D, Twomy C. Comparison of risperidone with trazodone in the management of behaviour disorder in demented elderly patients in a hospital setting: a pilot study [abstract]. Irish Journal of Medical Science 2004; Vol. 173, issue 3 Suppl 2:36. [CN‐00663745]
References to ongoing studies
NCT00260624 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT00260624. Escitalopram treatment of patients with agitated dementia. http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00260624 (accessed Aug 18 2010)..
NCT00898807 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT00898807. Citalopram for Agitation in Alzheimer's Disease (CitAD). http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00898807 (accessed 19 Aug 2010).
Additional references
Ayalon 2006
-
- Ayalon L, Gum AM, Felicano L, Arean PA. Effectiveness of nonpharmacological interventions for the management of neuropsychiatric symptoms in patients with dementia: a systematic review. Archives of Internal Medicine 2006;166(20):2182‐2188. - PubMed
Balestreri 2000
-
- Balestreri L, Grossberg A, Grossberg GT. Behavioral and Psychological Symptoms of Dementia as a Risk Factor for Nursing Home Placement. International Psychogeriatrics 2000;12(Supplement 1):59‐62.
Ballard 1997
-
- Ballard C, O'Brien J, Coope B, Fairburn A, Abid F, Wilcock G. A prospective study of psychotic symptoms in dementia sufferers: psychosis in dementia. International Psychogeriatrics 1997;9(1):57‐64. - PubMed
Ballard 2006
Berg 1998
-
- Berg L. Clinical dementia rating (CDR). Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1988;24:637‐639. - PubMed
Birks 2006
Canadian Study of Health and Aging 1994
Chung 2002
Cohen‐Mansfield 1986
-
- Cohen‐Mansfield J. Agitated behaviors in the elderly: II. Preliminary results in the cognitively deteriorated. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 1986;34(10):722‐727. - PubMed
Cohen‐Mansfield 1989
-
- Cohen‐Mansfield J, Marx MS, Rosenthal AS. A description of agitation in a nursing home. Journal of Gerontology (Medical Sciences) 1989;44(3):M77‐84. - PubMed
Condren 2001
-
- Condren RM, Cooney C. Use of drugs by old age psychiatrists in the treatment of psychotic and behavioral symptoms of dementia. Aging and Mental Health 2001;5(3):235‐241. - PubMed
Cummings 1994
-
- Cummings JL, Mega M, Gray K, Rosenberg‐Thompson S, Carusi DA, Gombein J. The Neuropsychiatric Inventory: comprehensive assessment of psychopathology in dementia. Neurology 1994;44(12):2308‐2314. - PubMed
Fabian 2004
-
- Fabian TJ, Amico JA, Kroboth PD, Mulsant BH, Corey SE, Begley AE, Bensasi SG, Weber E, Dew MA, Reynolds CF, Pollock BG. Paroxetine‐Induced Hyponatremia in Older Adults. Archives of Internal Medicine 2004;164(3):327‐332. - PubMed
Ferri 2005
Folstein 1975
-
- Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR. Mini‐mental state a practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. Journal of Psychiatric Research 1975;12(3):189‐198. - PubMed
Gill 2007
-
- Gill SS, Bronskill SE, Normand SL, Anderson GM, Sykora K, Lam K, Bell CM, Lee PE, Fischer HD, Herrmann N, Gurwitz JH, Rochon PA. Antipsychotic drug use and mortality in older adults with dementia. Annals of Internal Medicine 2007;146(11):775‐786. - PubMed
Gottfries 1982
-
- Gottfries CG, Brane G, Gullberg B, Steen G. A new rating scale for dementia syndromes. Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics 1982;1(4):311‐330. - PubMed
Greve 2005
-
- Greve M, O'Connor D. A survey of Australian and New Zealand old age psychiatrists preferred medications to treat behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia (BPSD). International Psychogeriatrics 2005;17(2):195‐205. - PubMed
Herrmann 2004
-
- Herrmann N, Lanctot KL, Khan LR. The role of norepinephrine in the behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia. Journal of Neuropsychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience 2004;16(3):261‐276. - PubMed
Herrmann 2007
-
- Herrmann N, Lanctot KL. Pharmacological Management of Neuropsychiatric Symptoms of Alzheimer Disease. Canadian Journal of Psychiatry 2007;52(10):630‐646. - PubMed
Hurt 2008
-
- Hurt C, Bhattacharyya S, Burns A, Camus V, Liperoti R, Marriott A, Nobili F, Robert P, Tsolaki M, Vellas B, Verhey F, Byrne EJ. Patient and caregiver perspectives of quality of life in dementia. An investigation of the relationship to behavioral and psychological symptoms in dementia. Dementia & Geriatric Cognitive Disorders 2008;26(2):138‐146. - PubMed
Jeste 2008
Lanctot 2001
-
- Lanctot KL, Herrmann N, Mazzotta P. Role of serotonin in the behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia. Journal of Neuropsychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience 2001;13(1):5‐21. - PubMed
Levin 1987
Livingston 2005
-
- Livingston G, Johnston K, Katona C, Paton J, Lyketosos CG. Systematic review of psychological approaches to the management of neuropsychiatric symptoms of dementia. American Journal of Psychiatry 2005;162(11):1996‐2021. - PubMed
Lonergan 2002
Lonergan 2004
Lyketsos 2002
-
- Lyketsos CG, Lopez O, Jones B, Fitzpatrick AL, Breitner J, DeKosky S. Prevalence of neuropsychiatric symptoms in dementia and mild cognitive impairment: results from the cardiovascular health study. JAMA 2002;288(12):1475‐1483. - PubMed
Martinón‐Torres 2004
McKeith 2005
-
- McKeith IG, Dickson DW, Lowe J, Emre M, O'Brien JT, Feldman H, et al. Diagnosis and management of dementia with Lewy bodies: third report of the DLB Consortium.. Neurology 2005;65(12):1863‐1872. - PubMed
McKhann 1984
-
- McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: report of the NINCDS‐ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of the Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's Disease. Neurology 1984;34(7):939‐944. - PubMed
McShane 2006
-
- McShane R, Areosa Sastre A, Minakaran N. Memantine for dementia. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2006, Issue 2. - PubMed
Nijk 2009
-
- Nijk RM, Zuidema SU, Koopmans RT. Prevalence and correlates of psychotropic drug use in Dutch nursing home patients with dementia.. International Psychogeriatrics 2009;21(3):485‐493. - PubMed
Panisset 1994
-
- Panisset M, Roudier M, Saxton J, Boiler F. Severe Impairment Battery: A neuropsychological test for severely demented patients. Archives of Neurology 1994;51:41‐45. - PubMed
Pitkala 2004
-
- Pitkala KH, Laurila JV, Strandber TE, Tilvis RS. Behavioral symptoms and the administration of psychotropic drugs to aged patients with dementia in nursing homes and in acute geriatric wards. International Psychogeriatrics 2004;16(1):61‐74. - PubMed
Plassman 2007
Richards 2007
-
- Richards JB, Papaioannou A, Adachi JD, Joseph L, Whitson HE, Prior JC, Goltzman D, Canadian Multicentre Osteoporosis Study Research Group. Effect of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors on the risk of fracture. Archives of Internal Medicine 2007;167(2):188‐194. - PubMed
Roman 1993
-
- Roman G, Tatemichi T, Erkinjunti T. Vascular dementia diagnostic criteria for research studies. Neurology 1993;43(2):250‐260. - PubMed
Rosen 1984
-
- Rosen WG, Mohs RC, Davis KL. A new rating scale for Alzheimer's disease. American Journal of Psychiatry 1984;141(11):1356‐1364. - PubMed
Sacchetti 2010
-
- Sacchetti E, Turrina C, Valsecchi P. Cerebrovascular Accidents in Elderly People Treated with Antipsychotic Drugs. Drug Safety 2010;33(4):273‐288. - PubMed
Salzman 2008
-
- Salzman C, Jeste DV, Meyer RE, Cohen‐Mansfield J, Cummings J, Grossberg GT, et al. Elderly patients with dementia‐related symptoms of severe agitation and aggression: consensus statement on treatment options, clinical trials methodology, and policy. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 2008;69(6):889‐898. - PMC - PubMed
Savva 2009
-
- Savva GM, Zaccai J, Matthews FE, Davidson JE, McKeith I, Brayne C, Medical Research Council Cognitive Function and Ageing Study. Prevalence, correlates, and course of behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia in the population. British Journal of Psychiatry 2009;194(3):212‐219. - PubMed
Schneider 2001
-
- Schneider LS, Tariot PN, Lyketsos CG, Dagerman KS, Davis KL, Davis S, Hsiao JK, Jeste DV, Katz IR, Olin JT, Pollock BG, Rabins PV, Rosenheck RA, Small GW, Lebowitz B, Lieberman, JA. National Institute of Mental Health Clinical Antipsychotic Trials of Intervention Effectiveness (CATIE): Alzheimer disease trial methodology. American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2001;9(4):346‐360. - PubMed
Schneider 2005
-
- Schneider LS, Dagerman KS, Insel P. Risk of death with atypical antipsychotics drug treatment for dementia: meta‐analysis of randomized placebo‐controlled trials. JAMA 2005;294(15):1934‐1943. - PubMed
Schneider 2006
-
- Schneider LS, Tariot PN, Dagerman KS, Davis SM, Hsiao JK, Ismail MS, Lebowitz BD, Lyketsos CG, Ryan JM, Stroup TS, Sultzer DL, Weintraub D, Lieberman JA, CATIE‐AD Study Group. Effectiveness of atypical antipsychotic drugs in patients with Alzheimer's disease. New England Journal of Medicine 2006;355(15):1525‐1538. - PubMed
Sclan 1996
-
- Sclan SG, Saillon A, Franseen E, Hogonot‐Diener L, Saillon A, Reisberg B. The Behavior Pathology in Alzheimer's Disease Rating Scale (BEHAVE‐AD): Reliability and Analysis of Symptom Category Scores. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 1996;11:819‐830.
Selbaek 2007
-
- Selbaek G, Kirkevold O, Engedal K. The prevalence of psychiatric symptoms and behavioral disturbances and the use of psychotropic drugs in Norwegian nursing homes. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2007;22(9):843‐849. - PubMed
Sink 2005
-
- Sink KM, Holden KF, Yaffe K. Pharmacological treatment of neuropsychiatric symptoms of dementia: a review of the evidence. JAMA 2005;293(5):596‐608. - PubMed
Steinberg 2004
-
- Steinberg M, Tschanz JT, Corcoran C, Steffens DC, Norton MC, Lyketsos CG, Breitner JC. The persistance of neuropsychiatric symptoms in dementia: the Cache County Study. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2004;19(1):19‐26. - PubMed
Tariot 1995
-
- Tariot PN, Mack JL, Patterson MB, Edland SD, Weiner MF, Fillenbaum G, Blazina L, Teri L, Rubin E, Mortimer JA. The Behavior Rating Scale for Dementia of the Consortium to Establish a Registry for Alzheimer's Disease. The Behavioral Pathology Committee of the Consortium to Establish a Registry for Alzheimer's Disease. American Journal of Psychiatry 1995;152(9):1349‐1357. - PubMed
van Walraven 2001
Vink 2003
Zuidema 2007
-
- Zuidema SU, Derksen E, Verhey FR, Koopmans RT. Prevalence of neuropsychiatric symptoms in a large sample of Dutch nursing home patients with dementia. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 2007;22(7):632‐638. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

