Taste bud cells of adult mice are responsive to Wnt/β-catenin signaling: implications for the renewal of mature taste cells
- PMID: 21328519
- PMCID: PMC3536498
- DOI: 10.1002/dvg.20731
Taste bud cells of adult mice are responsive to Wnt/β-catenin signaling: implications for the renewal of mature taste cells
Abstract
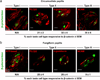
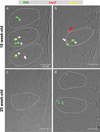
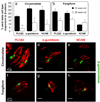
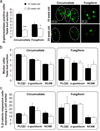
Wnt/β-catenin signaling initiates taste papilla development in mouse embryos, however, its involvement in taste cell turnover in adult mice has not been explored. Here we used the BATGAL reporter mouse model, which carries an engineered allele in which the LacZ gene is expressed in the presence of activated β-catenin, to determine the responsiveness of adult taste bud cells to canonical Wnt signaling. Double immunostaining with markers of differentiated taste cells revealed that a subset of Type I, II, and III taste cells express β-galactosidase. Using in situ hybridization, we showed that β-catenin activates the transcription of the LacZ gene mainly in intragemmal basal cells that are immature taste cells, identified by their expression of Sonic Hedgehog (Shh). Finally, we showed that β-catenin activity is significantly reduced in taste buds of 25-week-old mice compared with 10-week-old animals. Our data suggest that Wnt/β-catenin signaling may influence taste cell turnover by regulating cell differentiation. Reduced canonical Wnt signaling in older mice could explain in part the loss of taste sensitivity with aging, implicating a possible deficiency in the rate of taste cell renewal. More investigations are now necessary to understand if and how Wnt signaling regulates adult taste cell turnover.
Copyright © 2011 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
β-Catenin signaling regulates temporally discrete phases of anterior taste bud development.Development. 2015 Dec 15;142(24):4309-17. doi: 10.1242/dev.121012. Epub 2015 Nov 2. Development. 2015. PMID: 26525674 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt signaling interacts with Shh to regulate taste papilla development.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Feb 13;104(7):2253-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0607399104. Epub 2007 Feb 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17284610 Free PMC article.
-
Dosage-dependent hedgehog signals integrated with Wnt/beta-catenin signaling regulate external genitalia formation as an appendicular program.Development. 2009 Dec;136(23):3969-78. doi: 10.1242/dev.039438. Development. 2009. PMID: 19906864 Free PMC article.
-
Cell lineage and differentiation in taste buds.Arch Histol Cytol. 2006 Dec;69(4):209-25. doi: 10.1679/aohc.69.209. Arch Histol Cytol. 2006. PMID: 17287576 Review.
-
Crosstalk between Wnt/β-catenin and Hedgehog/Gli signaling pathways in colon cancer and implications for therapy.Cancer Biol Ther. 2015;16(1):1-7. doi: 10.4161/15384047.2014.972215. Cancer Biol Ther. 2015. PMID: 25692617 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
β-Catenin Signaling Biases Multipotent Lingual Epithelial Progenitors to Differentiate and Acquire Specific Taste Cell Fates.PLoS Genet. 2015 May 28;11(5):e1005208. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005208. eCollection 2015 May. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 26020789 Free PMC article.
-
Anterior and Posterior Tongue Regions and Taste Papillae: Distinct Roles and Regulatory Mechanisms with an Emphasis on Hedgehog Signaling and Antagonism.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 2;24(5):4833. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054833. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36902260 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sweet preference modified by early experience in mice and the related molecular modulations on the peripheral pathway.J Mol Neurosci. 2013 Sep;51(1):225-36. doi: 10.1007/s12031-013-0011-y. Epub 2013 Apr 19. J Mol Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23606220
-
Tongue and Taste Organ Biology and Function: Homeostasis Maintained by Hedgehog Signaling.Annu Rev Physiol. 2017 Feb 10;79:335-356. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-022516-034202. Annu Rev Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28192057 Free PMC article. Review.
-
WNT10A mutation causes ectodermal dysplasia by impairing progenitor cell proliferation and KLF4-mediated differentiation.Nat Commun. 2017 Jun 7;8:15397. doi: 10.1038/ncomms15397. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 28589954 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adler E, Hoon MA, Mueller KL, Chandrashekar J, Ryba NJP, Zuker CS. A Novel Family of Mammalian Taste Receptors. Cell. 2000;100:693–702. - PubMed
-
- Almeida M, Han L, Martin-Millan M, O'Brien CA, Manolagas SC. Oxidative Stress Antagonizes Wnt Signaling in Osteoblast Precursors by Diverting β-Catenin from T Cell Factor- to Forkhead Box O-mediated Transcription. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2007a;282:27298–27305. - PubMed
-
- Almeida M, Han L, Martin-Millan M, Plotkin LI, Stewart SA, Roberson PK, Kousteni S, O'Brien CA, Bellido T, Parfitt AM, Weinstein RS, Jilka RL, Manolagas SC. Skeletal Involution by Age-associated Oxidative Stress and Its Acceleration by Loss of Sex Steroids. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2007b;282:27285–27297. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Asano-Miyoshi M, Hamamichi R, Emori Y. Cytokeratin 14 is expressed in immature cells in rat taste buds. J Mol Histol. 2008;39:193–199. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

