Function and regulation of the Mediator complex
- PMID: 21330129
- PMCID: PMC3086004
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gde.2011.01.013
Function and regulation of the Mediator complex
Abstract
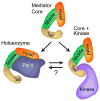
Over the past few years, advances in biochemical and genetic studies of the structure and function of the Mediator complex have shed new light on its subunit architecture and its mechanism of action in transcription by RNA polymerase II (pol II). The development of improved methods for reconstitution of recombinant Mediator subassemblies is enabling more in-depth analyses of basic features of the mechanisms by which Mediator interacts with and controls the activity of pol II and the general initiation factors. The discovery and characterization of multiple, functionally distinct forms of Mediator characterized by the presence or absence of the Cdk8 kinase module have led to new insights into how Mediator functions in both Pol II transcription activation and repression. Finally, progress in studies of the mechanisms by which the transcriptional activation domains (ADs) of DNA binding transcription factors target Mediator have brought to light unexpected complexities in the way Mediator participates in signal transduction.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Myers LC, Kornberg RD. Mediator of Transcriptional Regulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 2000;69:729–749. - PubMed
-
- Backstrom S, Elfving N, Nilsson R, Wingsle G, Bjorklund S. Purification of a plant mediator from Arabidopsis thaliana identifies PFT1 as the Med25 subunit. Mol Cell. 2007;26:717–729. - PubMed
-
This paper describes the first purification and characterization of Mediator from plants. The authors' findings illustrate the remarkable evolutionary conservation of plant and animal Mediator complexes.
-
- Sato S, Tomomori-Sato C, Parmely TJ, Florens L, Zybailov B, Swanson SK, Banks CA, Jin J, Cai Y, Washburn MP, Conaway JW, Conaway RC. A set of consensus mammalian mediator subunits identified by multidimensional protein identification technology. Mol Cell. 2004;14:685–691. - PubMed
-
- Bourbon HM. Comparative genomics supports a deep evolutionary origin for the large, four-module transcriptional mediator complex. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36:3993–4008. - PMC - PubMed
-
This paper provides an in-depth bioinformatic comparison of Mediator subunits across species. The author's findings reveal the evolutionary conservation and ancient origin of Mediator in eukaryotes.
-
- Malik S, Roeder RG. Dynamic regulation of pol II transcription by the mammalian Mediator complex. Trends Biochem Sci. 2005;30:256–263. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

