DENN domain proteins: regulators of Rab GTPases
- PMID: 21330364
- PMCID: PMC3077579
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.R110.217067
DENN domain proteins: regulators of Rab GTPases
Abstract
The DENN domain is a common, evolutionarily ancient, and conserved protein module, yet it has gone largely unstudied; until recently, little was known regarding its functional roles. New studies reveal that various DENN domains interact directly with members of the Rab family of small GTPases and that DENN domains function enzymatically as Rab-specific guanine nucleotide exchange factors. Thus, DENN domain proteins appear to be generalized regulators of Rab function. Study of these proteins will provide new insights into Rab-mediated membrane trafficking pathways.
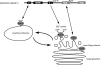
Figures



References
-
- Pawson T., Nash P. (2003) Science 300, 445–452 - PubMed
-
- Levivier E., Goud B., Souchet M., Calmels T. P., Mornon J. P., Callebaut I. (2001) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 287, 688–695 - PubMed
-
- Stenmark H. (2009) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 10, 513–525 - PubMed
-
- Zerial M., McBride H. (2001) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2, 107–117 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

