Multiple sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins mediate estrogen receptor signaling through a tethering pathway
- PMID: 21330404
- PMCID: PMC3063082
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2010-0425
Multiple sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins mediate estrogen receptor signaling through a tethering pathway
Abstract
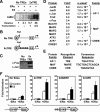
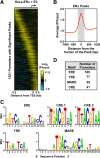
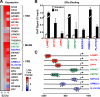
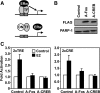
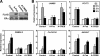
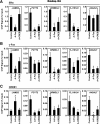
The indirect recruitment (tethering) of estrogen receptors (ERs) to DNA through other DNA-bound transcription factors (e.g. activator protein 1) is an important component of estrogen-signaling pathways, but our understanding of the mechanisms of ligand-dependent activation in this pathway is limited. Using proteomic, genomic, and gene-specific analyses, we demonstrate that a large repertoire of DNA-binding transcription factors contribute to estrogen signaling through the tethering pathway. In addition, we define a set of endogenous genes for which ERα tethering through activator protein 1 (e.g. c-Fos) and cAMP response element-binding protein family members mediates estrogen responsiveness. Finally, we show that functional interplay between c-Fos and cAMP response element-binding protein 1 contributes to estrogen-dependent regulation through the tethering pathway. Based on our results, we conclude that ERα recruitment in the tethering pathway is dependent on the ligand-induced formation of transcription factor complexes that involves interplay between the transcription factors from different protein families.
Figures
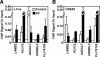
References
-
- Heldring N, Pike A, Andersson S, Matthews J, Cheng G, Hartman J, Tujague M, Ström A, Treuter E, Warner M, Gustafsson JA. 2007. Estrogen receptors: how do they signal and what are their targets. Physiol Rev 87:905–931 - PubMed
-
- Jakacka M, Ito M, Martinson F, Ishikawa T, Lee EJ, Jameson JL. 2002. An estrogen receptor (ER)α deoxyribonucleic acid-binding domain knock-in mutation provides evidence for nonclassical ER pathway signaling in vivo. Mol Endocrinol 16:2188–2201 - PubMed
-
- O'Brien JE, Peterson TJ, Tong MH, Lee EJ, Pfaff LE, Hewitt SC, Korach KS, Weiss J, Jameson JL. 2006. Estrogen-induced proliferation of uterine epithelial cells is independent of estrogen receptor α binding to classical estrogen response elements. J Biol Chem 281:26683–26692 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

