Therapeutic hypothermia: critical review of the molecular mechanisms of action
- PMID: 21331282
- PMCID: PMC3035015
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2011.00004
Therapeutic hypothermia: critical review of the molecular mechanisms of action
Abstract
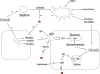
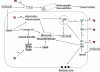
Therapeutic hypothermia (TH) is nowadays one of the most important methods of neuroprotection. The events that occur after an episode of ischemia are multiple and hypothermia can affect the various steps of this cascade. The mechanisms of action of TH are varied and the possible explanation for the benefits of this therapy is probably the multiple mechanisms of action blocking the cascade of ischemia on many levels. TH can affect many metabolic pathways, reactions of inflammation, apoptosis processes, and promote neuronal integrity. To know the mechanisms of action of TH will allow a better understanding about the indications for this therapy and the possibility of searching for other therapies when used in conjunction with hypothermia will provide a therapeutic synergistic effect.
Keywords: cerebral ischemia; excitatory neurotransmitters; mechanism of action; neuronal acidosis; neuronal death; therapeutic hypothermia.
Figures

References
-
- Baker A. J., Zornow M. H., Grafe M. R., Scheller M. S., Skilling S. R., Smullin D. H., Larson A. A. (1991). Hypothermia prevents ischemia-induced increases in hippocampal glycine concentrations in rabbits. Stroke 22, 666–673 - PubMed
-
- Bargonetti J., Manfredi J. J. (2002). Multiple roles of the tumor suppressor p53. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 14, 86–91 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

