A Sequential Model of Host Cell Killing and Phagocytosis by Entamoeba histolytica
- PMID: 21331284
- PMCID: PMC3038552
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/926706
A Sequential Model of Host Cell Killing and Phagocytosis by Entamoeba histolytica
Abstract
The protozoan parasite Entamoeba histolytica is responsible for invasive intestinal and extraintestinal amebiasis. The virulence of Entamoeba histolytica is strongly correlated with the parasite's capacity to effectively kill and phagocytose host cells. The process by which host cells are killed and phagocytosed follows a sequential model of adherence, cell killing, initiation of phagocytosis, and engulfment. This paper presents recent advances in the cytolytic and phagocytic processes of Entamoeba histolytica in context of the sequential model.
Figures
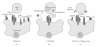

References
-
- WHO/PAHO/UNESCO report. A consultation with experts on amoebiasis. Mexico City, Mexico 28-29 January, 1997. Epidemiological Bulletin. 1997;18(1):13–14. - PubMed
-
- Haque R, Huston CD, Hughes M, Houpt E, Petri WA., Jr. Amebiasis. New England Journal of Medicine. 2003;348(16):1565–1573. - PubMed
-
- Campos-Rodríguezp R, Jarillo-Luna A. The pathogenicity of Entamoeba histolytica is related to the capacity of evading innate immunity. Parasite Immunology. 2005;27(1-2):1–8. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

