FGF21 as an Endocrine Regulator in Lipid Metabolism: From Molecular Evolution to Physiology and Pathophysiology
- PMID: 21331285
- PMCID: PMC3038562
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/981315
FGF21 as an Endocrine Regulator in Lipid Metabolism: From Molecular Evolution to Physiology and Pathophysiology
Abstract
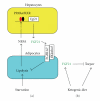
The FGF family comprises twenty-two structurally related proteins with functions in development and metabolism. The Fgf21 gene was generated early in vertebrate evolution. FGF21 acts as an endocrine regulator in lipid metabolism. Hepatic Fgf21 expression is markedly induced in mice by fasting or a ketogenic diet. Experiments with Fgf21 transgenic mice and cultured cells indicate that FGF21 exerts pharmacological effects on glucose and lipid metabolism in hepatocytes and adipocytes via cell surface FGF receptors. However, experiments with Fgf21 knockout mice indicate that FGF21 inhibits lipolysis in adipocytes during fasting and attenuates torpor induced by a ketogenic diet but maybe not a physiological regulator for these hepatic functions. These findings suggest the pharmacological effects to be distinct from the physiological roles. Serum FGF21 levels are increased in patients with metabolic diseases having insulin resistance, indicating that FGF21 is a metabolic regulator and a biomarker for these diseases.
Figures

References
-
- Gospodarowicz D. Purification of a fibroblast growth factor from bovine pituitary. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1975;250(7):2515–2520. - PubMed
-
- Gospodarowicz D, Bialecki H, Greenburg G. Purification of the fibroblast growth factor activity from bovine brain. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1978;253(10):3736–3743. - PubMed
-
- Itoh N, Ornitz DM. Evolution of the Fgf and Fgfr gene families. Trends in Genetics. 2004;20(11):563–569. - PubMed
-
- Itoh N, Ornitz DM. Functional evolutionary history of the mouse Fgf gene family. Developmental Dynamics. 2008;237(1):18–27. - PubMed
-
- Itoh N. The Fgf families in humans, mice, and zebrafish: their evolutional processes and roles in development, metabolism, and disease. Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin. 2007;30(10):1819–1825. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

