Varenicline attenuates cue-induced relapse to alcohol, but not nicotine seeking, while reducing inhibitory response control
- PMID: 21331520
- PMCID: PMC3121941
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-011-2213-8
Varenicline attenuates cue-induced relapse to alcohol, but not nicotine seeking, while reducing inhibitory response control
Abstract
Rationale: Treatment of the most widely abused drugs, nicotine and alcohol, is hampered by high rates of relapse. Varenicline tartrate, an α4β2 nicotinic receptor partial agonist, is currently prescribed as a smoking cessation aid. However, there is emerging evidence that it may also modulate alcohol seeking and cognitive functioning in rats.
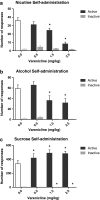
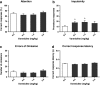
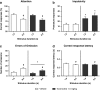
Objectives: As preclinical data on alcohol taking and relapse are limited, we used a self-administration-reinstatement model to evaluate the effects of varenicline on operant responding for alcohol (12%, v/v), intravenous nicotine (40 μg/kg/inf.), sucrose (10%, w/v) and on cue-induced relapse to alcohol and nicotine seeking in rats. At the cognitive level, we assed varenicline's effects on 5-choice serial reaction time task (5-CSRTT) performance with a focus on correct responses (attention) and premature responding (impulsivity), modalities that have previously been associated with addictive behaviour.
Results: Varenicline, at doses of 1.5 and 2.5 mg/kg, reduced alcohol and nicotine self-administration and enhanced operant responding for sucrose. At these doses, varenicline reduced cue-induced relapse to alcohol, but not nicotine seeking. In contrast, at 0.5 mg/kg, varenicline facilitated cue-induced nicotine seeking. Similar to nicotine, varenicline increased premature responding at low doses, but had no effect on any of the other behavioural parameters in the 5-CSRTT.
Conclusions: Our data indicate that varenicline specifically reduced responding for nicotine and alcohol, but not for natural reinforcers such as sucrose. Interestingly, varenicline strongly attenuated cue-induced relapse to alcohol seeking, but not nicotine seeking. Varenicline may therefore be a promising aid in the treatment of alcohol addiction.
Figures
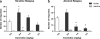
References
-
- Anton RF, O'Malley SS, Ciraulo DA, Cisler RA, Couper D, Donovan DM, Gastfriend DR, Hosking JD, Johnson BA, LoCastro JS, Longabaugh R, Mason BJ, Mattson ME, Miller WR, Pettinati HM, Randall CL, Swift R, Weiss RD, Williams LD, Zweben A. Combined pharmacotherapies and behavioral interventions for alcohol dependence: the COMBINE study: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2006;295:2003–2017. doi: 10.1001/jama.295.17.2003. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chatterjee S, Steensland P, Simms JA, Holgate J, Coe JW, Hurst RS, Shaffer CL, Lowe J, Rollema H, Bartlett SE. Partial agonists of the α3β4* neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor reduce ethanol consumption and seeking in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2011;36:603–615. doi: 10.1038/npp.2010.191. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

