CaMKII regulates pericyte loss in the retina of early diabetic mouse
- PMID: 21331776
- PMCID: PMC3932701
- DOI: 10.1007/s10059-011-0038-2
CaMKII regulates pericyte loss in the retina of early diabetic mouse
Abstract
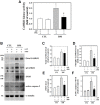
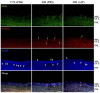
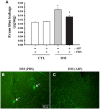
Inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) is an essential mediator in diabetic vascular lesions and known to be regulated by activation of Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII). The aim of this study was to investigate whether CaMKII affects iNOS-mediated pericyte death in the retina of diabetic mice with early stage disease. Total- and phospho-CaMKII, iNOS, and active caspase-3 protein levels were assessed by Western blotting, and CaMKII activity was measured by kinase assay. iNOS-related pericyte death was assessed by double immunofluorescent staining for iNOS and α-smooth muscle actin, followed by the TUNEL assay. Autocamtide-2-related inhibitory peptide (AIP), a specific inhibitor of CaMKII, was injected into the right vitreous 2 days before sacrifice of mice, to examine the effect of CaMKII inactivation in diabetic retinas. The levels of total- and phospho-CaMKII, iNOS, and active caspase-3 protein, and CaMKII activity were significantly increased in the diabetic retinas compared with those of control retinas. Furthermore, TUNEL-positive signals colocalized with iNOS-immunoreactive pericytes in the same retinas. However, inactivation of CaMKII by AIP treatment inhibited all these changes, which was accompanied by less pericyte loss. Our results demonstrate that CaMKII contributes to iNOS-related death of pericytes in the diabetic retina and that inactivation of this enzyme may be a potential treatment for retinal vascular lesion.
Figures
References
-
- Aromolaran A.A., Blatter L.A. Modulation of intracellular Ca2+ release and capacitative Ca2+ entry by CaMKII inhibitors in bovine vascular endothelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. (2005);289:C1426–1436. - PubMed
-
- Benter I.F., Yousif M.H., Canatan H., Akhtar S. Inhibition of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II, RASGTPase and 20-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid attenuates the development of diabetes-induced vascular dysfunction in the rat carotid artery. Pharmacol. Res. (2005);52:252–257. - PubMed
-
- Carmo A., Cunha-Vaz J.G., Carvalho A.P., Lopes M.C. Nitric oxide synthase activity in retinas from non-insulindependent diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rats: correlation with bloodretinal barrier permeability. Nitric Oxide. (2000);4:590–596. - PubMed
-
- Cheung A.K., Fung M.K., Lo A.C., Lam T.T., So K.F., Chung S.S., Chung S.K. Aldose reductase deficiency prevents diabetes-induced blood-retinal barrier breakdown, apoptosis, and glial reactivation in the retina of db/db mice. Diabetes. (2005);54:3119–3125. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

