A phase 2 study of (99m)Tc-tilmanocept in the detection of sentinel lymph nodes in melanoma and breast cancer
- PMID: 21331809
- PMCID: PMC3071527
- DOI: 10.1245/s10434-010-1524-z
A phase 2 study of (99m)Tc-tilmanocept in the detection of sentinel lymph nodes in melanoma and breast cancer
Abstract
Background: Several (99m)Tc-labeled agents that are not approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration are used for lymphatic mapping. A new low-molecular-weight mannose receptor-based, reticuloendothelial cell-directed, (99m)Tc-labeled lymphatic imaging agent, (99m)Tc-tilmanocept, was used for lymphatic mapping of sentinel lymph nodes (SLNs) from patients with primary breast cancer or melanoma malignancies. This novel molecular species provides the basis for potentially enhanced SLN mapping reliability.
Methods: In a prospectively planned, open-label phase 2 clinical study, (99m)Tc-tilmanocept was injected into breast cancer and cutaneous melanoma patients before intraoperative lymphatic mapping. Injection technique, preoperative lymphoscintigraphy (LS), and intraoperative lymphatic mapping with a handheld gamma detection probe were performed by investigators per standard practice.
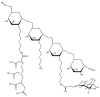
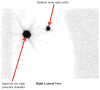
Results: Seventy-eight patients underwent (99m)Tc-tilmanocept injection and were evaluated (47 melanoma, 31 breast cancer). For those whom LS was performed (55 patients, 70.5%), a (99m)Tc-tilmanocept hot spot was identified in 94.5% of LS patients before surgery. Intraoperatively, (99m)Tc-tilmanocept identified at least one regional SLN in 75 (96.2%) of 78 patients: 46 (97.9%) of 47 in melanoma and 29 (93.5%) of 31 in breast cancer cases. Tissue specificity of (99m)Tc-tilmanocept for lymph nodes was 100%, displaying 95.1% mapping sensitivity by localizing in 173 of 182 nodes removed during surgery. The overall proportion of (99m)Tc-tilmanocept-identified nodes that contained metastatic disease was 13.7%. Five procedure-related serious adverse events occurred, none related to (99m)Tc-tilmanocept.
Conclusions: Our results demonstrate the safety and efficacy of (99m)Tc-tilmanocept for use in intraoperative lymphatic mapping. The high intraoperative localization and lymph node specificity of (99m)Tc-tilmanocept and the identification of metastatic disease within the nodes suggest SLNs are effectively identified by this novel mannose receptor-targeted molecule.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Leong SP, Donegan E, Heffernon W, Dean S, Katz JA. Adverse reactions to isosulfan blue during selective sentinel lymph node dissection in melanoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2000;7:361–6. - PubMed
-
- Komenaka IK, Bauer VP, Schnabel FR, et al. Allergic reactions to isosulfan blue in sentinel lymph node mapping. Breast J. 2005;11:70–2. - PubMed
-
- King TA, Fey JV, Van Zee KJ, et al. A prospective analysis of the effect of blue-dye volume on sentinel lymph node mapping success and incidence of allergic reaction in patients with breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2004;11:535–41. - PubMed
-
- Scherer K, Studer W, Figueiredo V, Bircher AJ. Anaphylaxis to isosulfan blue and cross-reactivity to patent blue v: case report and review of the nomenclature of vital blue dyes. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2006;96:497–500. - PubMed
-
- Efron P, Knudsen E, Hirshorn S, Copeland EM. Anaphylactic reaction to isosulfan blue used for sentinel node biopsy: case report and literature review. Breast J. 2002;8:396–99. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

